植物雌雄异株性别决定研究进展
|
|
彭丹, 武志强
|
Progress on sex determination of dioecious plants
|
|
Dan Peng, Zhiqiang Wu
|
|
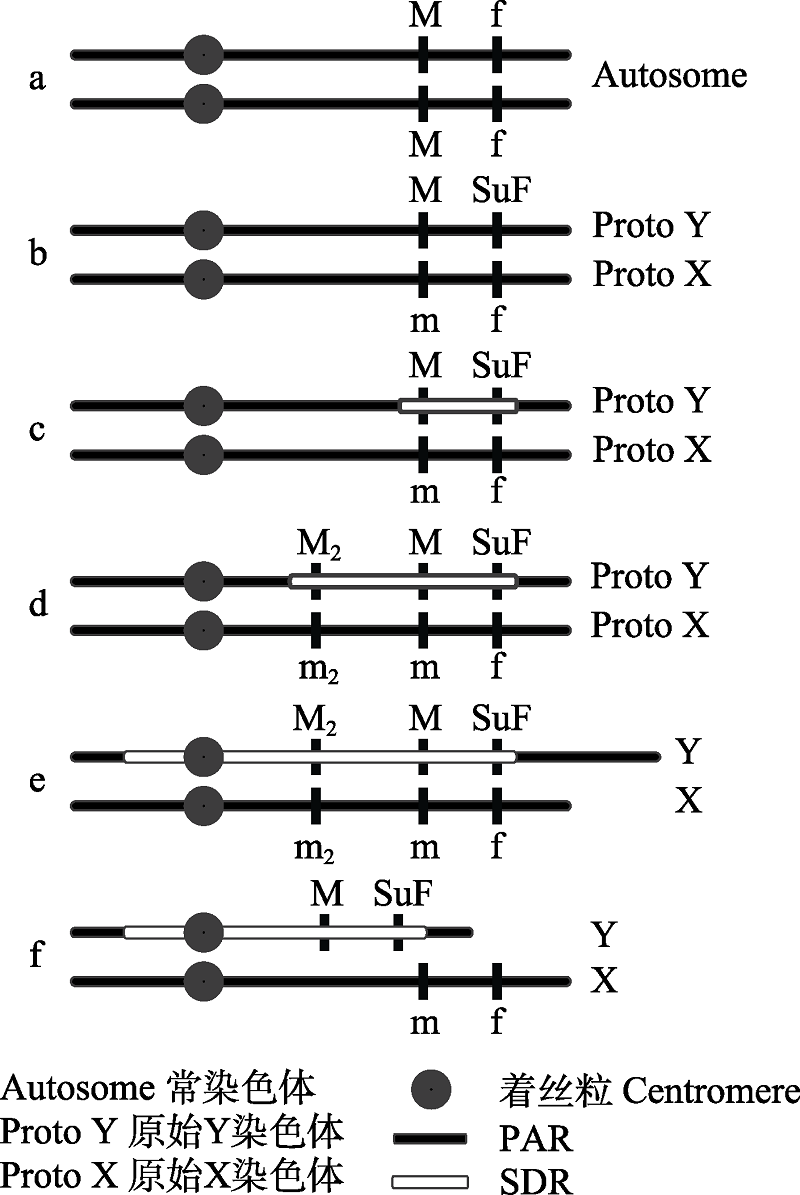
图2 性染色体进化推论(改编自Ming et al (2011))。a, 常染色体; b, 两个性别决定基因形成; c, 性别决定基因连锁, 形成初步性别决定区域; d, 更多性别相关基因连锁, 性别决定区域扩大; e, 由于重复序列累积, Y染色体增长; f, Y染色体退化; PAR, 拟常染色体区域; SDR, 性别决定区域; f→SuF为显性突变, M→m为隐性突变; M2→m2为雄性功能基因的隐性突变。
|
Fig. 2 Sex chromosome evolution corollary (adapted from Ming et al (2011)). a, Autosomes; b, Two sex-determining genes are formed; c, Sex determination genes are linked, forming a preliminary sex determination region; d, More sex related genes are linked, and the sex-determined region expands; e, The Y chromosome increases due to the accumulation of repeated sequences; f, Y chromosome degeneration; PAR, Pseudoautosomal regions; SDR, Sex-determined area. ‘f’ to ‘SuF’ is a dominant mutation, and ‘M’ to ‘m’ is a recessive mutation. ‘M2’ to ‘m2’ is a recessive mutation of another male functional gene.
|
|
|
|
|

