全球视角下的中国生物多样性监测进展与展望
Progress and prospect of China biodiversity monitoring from a global perspective
全球视角下的中国生物多样性监测进展与展望 |
| 吴慧, 徐学红, 冯晓娟, 米湘成, 苏艳军, 肖治术, 朱朝东, 曹垒, 高欣, 宋创业, 郭良栋, 吴东辉, 江建平, 沈浩, 马克平 |
|
Progress and prospect of China biodiversity monitoring from a global perspective |
| Hui Wu, Xuehong Xu, Xiaojuan Feng, Xiangcheng Mi, Yanjun Su, Zhishu Xiao, Chaodong Zhu, Lei Cao, Xin Gao, Chuangye Song, Liangdong Guo, Donghui Wu, Jianping Jiang, Hao Shen, Keping Ma |
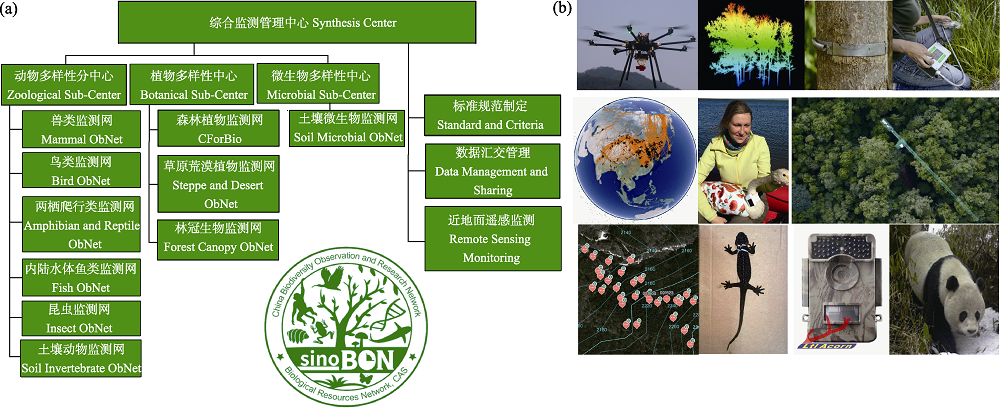
| 图2 Sino BON 10个专项网(a)在全国30个主点60个辅点对物种、群落和生态系统的动态变化以及多营养级之间互作进行监测, 并通过使用近地面遥感的无人机、测量树木生长的生长环、用于迁徙鸟类的卫星追踪器、用于林冠生物多样性监测的森林塔吊、用于两栖动物的无线电全频跟踪定位仪、用于哺乳动物和地栖鸟类监测的红外相机等设备打造了天-空-地一体化、长时序自动化监测的体系(b)。 |
| Fig. 2 An illustration of how Sino BON is organized for monitoring dynamics of species and ecosystems and multiple trophic interactions through cooperation among the 10 subnetworks (a), and through the use of UAVs for near-ground remote sensing, growth rings for measuring tree growth, satellite trackers for migratory birds, forest tower cranes for canopy biodiversity monitoring, radio full-frequency tracking locators for amphibians, and infrared cameras for mammal and terrestrial bird monitoring to build a sky-ground integrated and long-term automatic monitoring system (b). |

|