主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议
Principles, error sources and application suggestions of prevailing molecular dating methods
主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议 |
| 陈旸康, 王益, 李家亮, 王文韬, 冯端宇, 毛康珊 |
|
Principles, error sources and application suggestions of prevailing molecular dating methods |
| Yangkang Chen, Yi Wang, Jialiang Li, Wentao Wang, Duanyu Feng, Kangshan Mao |
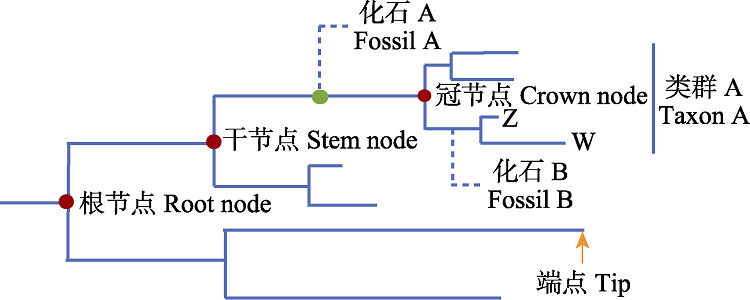
| 图3 系统发育树中部分术语示意图。图中冠节点的年龄代表了类群A现存所有物种最近共同祖先的节点, 而干节点代表了该类群最近共同祖先与其最近缘类群共祖的节点。以衍征法为例, 图中的化石A与类群A现存物种存在共同衍征, 因此可以作为类群A干节点的最小年龄限制; 而要为类群A的冠节点添加年龄限制, 需要获得与类群A的亚类群具有共同衍征的化石记录, 如图中的物种Z、W和化石B所表示的关系。系统发育法同理。 |
| Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of some terms in phylogenetic tree. The age of the crown node in the figure represents the node of the nearest common ancestor of all species in group A, while the stem node represents the node of the nearest common ancestor of the group A and its nearest related group. Taking the apomorphy-based method as an example, fossil A in the figure has synapomorphies with the extant species of group A, so it can be used as the minimum age constraint for the stem node of group A. To apply age constraint to the crown node of group A, it is necessary to obtain fossil records sharing synapomorphies with subgroups of group A, as indicated by the relationship of species Z, W and fossil B in the figure. The same is true of phylogenetic method. |

|