主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议
|
|
陈旸康, 王益, 李家亮, 王文韬, 冯端宇, 毛康珊
|
Principles, error sources and application suggestions of prevailing molecular dating methods
|
|
Yangkang Chen, Yi Wang, Jialiang Li, Wentao Wang, Duanyu Feng, Kangshan Mao
|
|
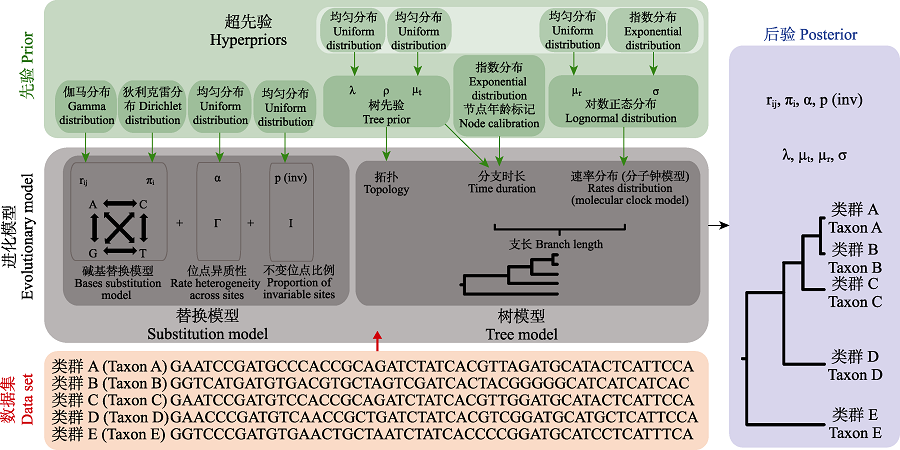
图1 贝叶斯法时间树构建过程示意图(改自: Bromham et al, 2018)。进化模型的参数设置是贝叶斯法系统发育树构建的关键步骤, 由替换模型和树模型组成。替换模型包括了碱基替换模型(包括碱基转换速率rij和碱基频率πi参数)、速率的位点(sites)异质型(如Γ分布)以及不变位点的比例p(inv)。树模型可以解构为结构与支长两个组份。结构由树先验决定, 图中使用的是生灭过程模型, 包含物种生成率(λ)、物种灭绝率(μt)和取样频率(ρ)三个参数。在“两步法”中, 结构还可以来自于树文件的输入。支长由分支时长与速率分布共同决定。分支时长一方面受树先验的影响, 另一方面与节点年龄标记密切相关; 速率分布即分子钟模型, 决定了进化速率在不同支上的分布格局。数据集与进化模型共同计算得到各参数的后验及时间树。
|
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of Bayesian time tree construction (modified from: Bromham et al, 2018). The parameter setting of evolutionary models is the key step of constructing phylogenetic tree based on Bayesian method, which is composed of substitution model and tree model. The substitution model includes base substitution model (including base conversion rate rij and base frequency πi as parameters), site heterogeneity of rate (such as Γ distribution) and proportion of invariant sites p(inv). The tree model can be decomposed into two components: structure and branch lengths. The structure is determined by tree priors (in this case the birth and death process model), which includes three parameters: species generation rate (λ), species extinction rate (μt) and sampling frequency (ρ). In the “two-step” method, the structure can also come from the input of the tree file. The branch length is determined by the branch duration and the rate distribution across branches. The branch duration is influenced by tree priors and node age calibration. The rate distribution is recognized as clock models, which determine the distribution pattern of evolution rate on different branches. The data set is applied to the evolutionary model to generate posteriors of each parameter and the time tree.
|
|
|
|
|

