南亚热带常绿阔叶林树木多样性与生物量和生产力的关联及其影响因素
Relationships between tree diversity and biomass/productivity and their influence factors in a lower subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest
南亚热带常绿阔叶林树木多样性与生物量和生产力的关联及其影响因素 |
| 朱杰, 吴安驰, 邹顺, 熊鑫, 刘世忠, 褚国伟, 张倩媚, 刘菊秀, 唐旭利, 闫俊华, 张德强, 周国逸 |
|
Relationships between tree diversity and biomass/productivity and their influence factors in a lower subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest |
| Jie Zhu, Anchi Wu, Shun Zou, Xin Xiong, Shizhong Liu, Guowei Chu, Qianmei Zhang, Juxiu Liu, Xuli Tang, Junhua Yan, Deqiang Zhang, Guoyi Zhou |
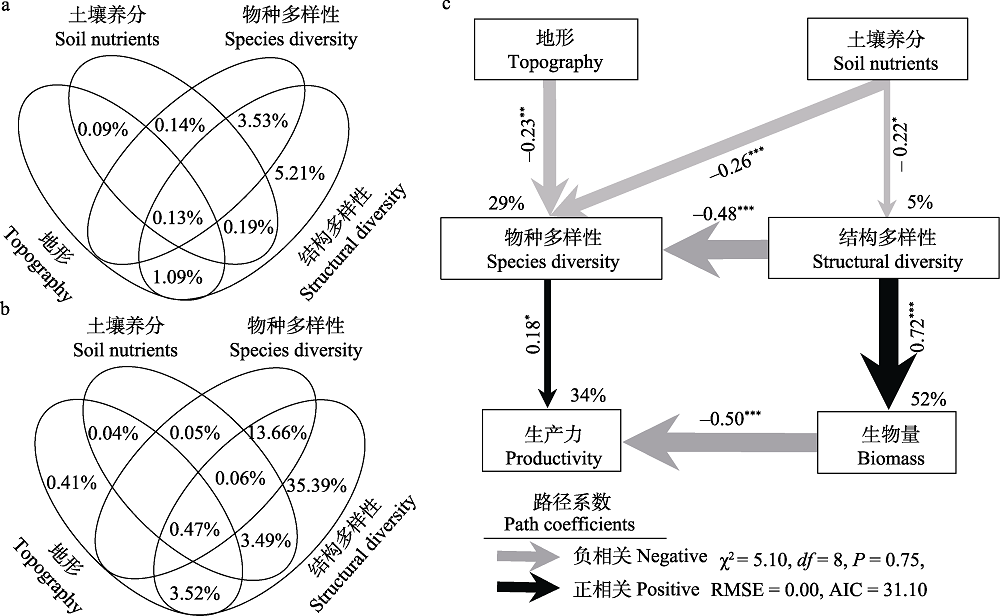
| 图3 物种多样性、结构多样性、地形和土壤养分对生产力和生物量的影响。(a)方差分解解释各因子对生产力的单独效应和共同效应; (b)方差分解解释各因子对生物量的单独效应和共同效应; (c)结构方程模型(SEM)解释地形和土壤养分通过物种多样性和结构多样性对生产力的直接和间接影响(N = 100)。SEM考虑了所有可能的路径, R2表示所解释的方差比例。箭头上的数字表示标准化的路径系数。箭头宽度表示路径系数的强度。*, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001。 |
| Fig. 3 The impact of species diversity, structural diversity, topography and soil nutrients on plant productivity and biomass. (a) Variation partitioning analysis explains the pure and shared effect of factors on plant productivity. (b) Variation partitioning analysis explains the pure and shared effect of factors on plant biomass. (c) Structural equation model (SEM) reveals the direct and indirect effects of species diversity, structural diversity, topography and soil nutrients on plant productivity and biomass (N = 100). The SEM considered all plausible pathways, to increase the degrees of freedom, R2 indicates the proportion of variance explained. The numbers on the arrows indicate standardized path coefficients. The arrow width is proportional to the strength of the path coefficients. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001. |

|