生态系统的多稳态与突变
Alternative stable states and tipping points of ecosystems
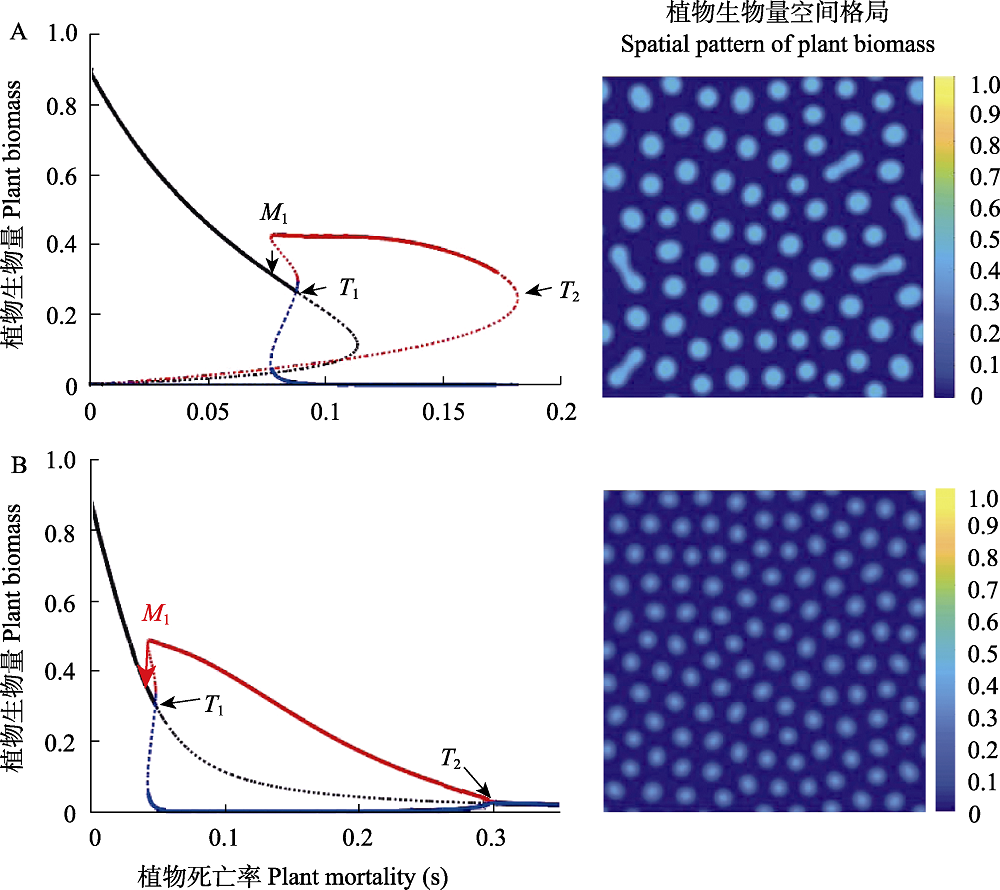
图3. 一个淡水沼泽湿地生态系统中产生的植物空间自组织格局与稳态转换。当系统中存在促进作用时可能同时产生多稳态和自组织空间格局特征。(A)和(B)分别是
Fig. 3. Spatial self-organization and alternative stable states of the plants in a freshwater wetland ecosystem. Facilitative effects may give rise to alternative stable states and spatial self-organization signature in ecosystems. (A) and (B) are regime shift and regular spatial patterns generated by the model 2 and 3 in table 1, respectively. M and T are bifurcation points (Adapted from