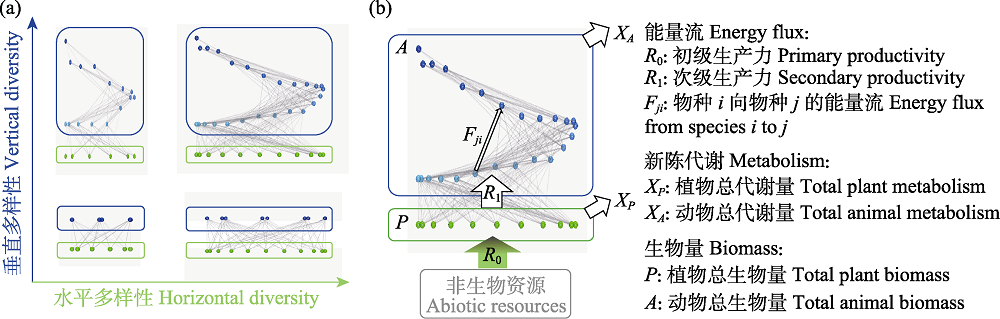
图2. 食物网中的生物多样性(a)和功能(b)。在食物网中, 生物多样性可通过水平多样性(如同一营养级内的物种数)和垂直多样性(如食物网的最高营养级)度量, 功能可通过营养级或物种之间的能量流、植物或动物的总代谢量和生物量刻画。其中, 非生物资源与植物群落(绿色框)之间的能量流表征了初级生产力, 植物与动物群落(蓝色框)之间的能量流表征了次级生产力。修改自
Fig. 2. Food web diversity (a) and functioning (b). Biodiversity in food webs can be measured by both horizontal diversity (e.g. species richness within trophic levels) and vertical diversity (e.g. the maximum trophic level). Functioning can be measured by energy fluxes between two trophic levels or two species, total plant or animal metabolism, and total plant or animal biomass. Specifically, the energy flux from abiotic resource to plant communities (green box) represents the primary productivity, and that from plant communities to animal communities (blue box) represents the secondary productivity. Modified from