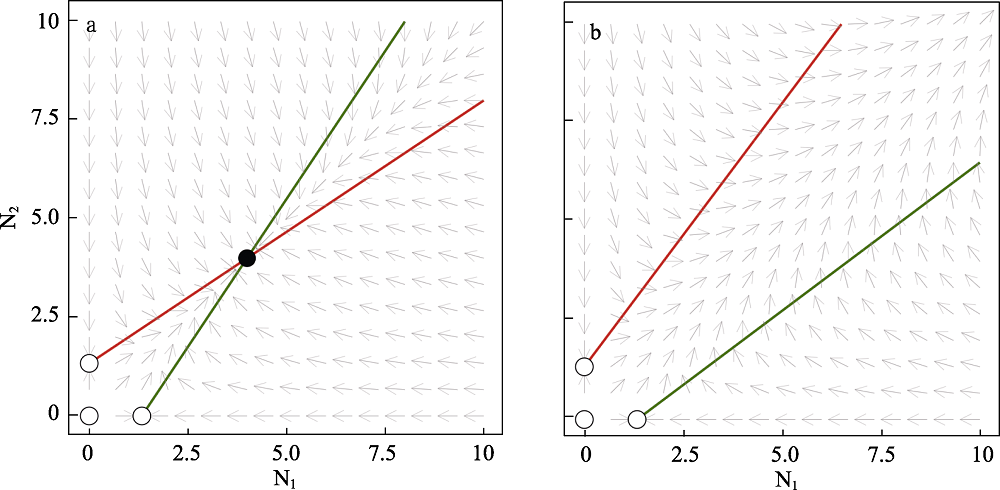
图2. 互惠种群N1和N2的相平面。a. 当雅各比行列式det(J) > 0时, 相互作用导致稳定的非平凡平衡(r1 = r2 = 2, a11 = a22 = -1.5, a12 = a21 = 1)。b. 当雅各比行列式det(J) < 0时, 相互作用导致种群数量无限增长的非稳定动态(r1 = r2 = 2, a11 = a22 = -1.5, a12 = a21 = 2)。种群N1的零增长等值线用绿色, N2的零增长等值线用红色。黑色填充圆表示稳定平衡点, 白色填充圆表示非稳定和半稳定(鞍点)平衡点, 灰色箭头表示种群变化方向。绘图软件Julia 1.4.1。
Fig. 2. Phase planes of mutualistic interactions between population N1 and N2. a. The mutualistic interaction leads to stable nontrivial equilibrium when det(J) > 0 (r1 = r2 = 2, a11 = a22 = -1.5, a12 = a21 = 1). b. The mutualistic interaction leads to non-stable dynamics (infinite populations size) when det(J) < 0 (r1 = r2 = 2, a11 = a22 = -1.5, a12 = a21 = 2). The nullcline of population N1 is labeled in green and N2 in red. Black-filled circle denotes stable equilibrium while white-filled circles denote non-stable and half-stable (saddle points) equilibria. Plots are made in Julia 1.4.1.