地形和土壤特性对亚热带常绿阔叶林内植物功能性状的影响
Effects of topographic variations and soil characteristics on plant functional traits in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest
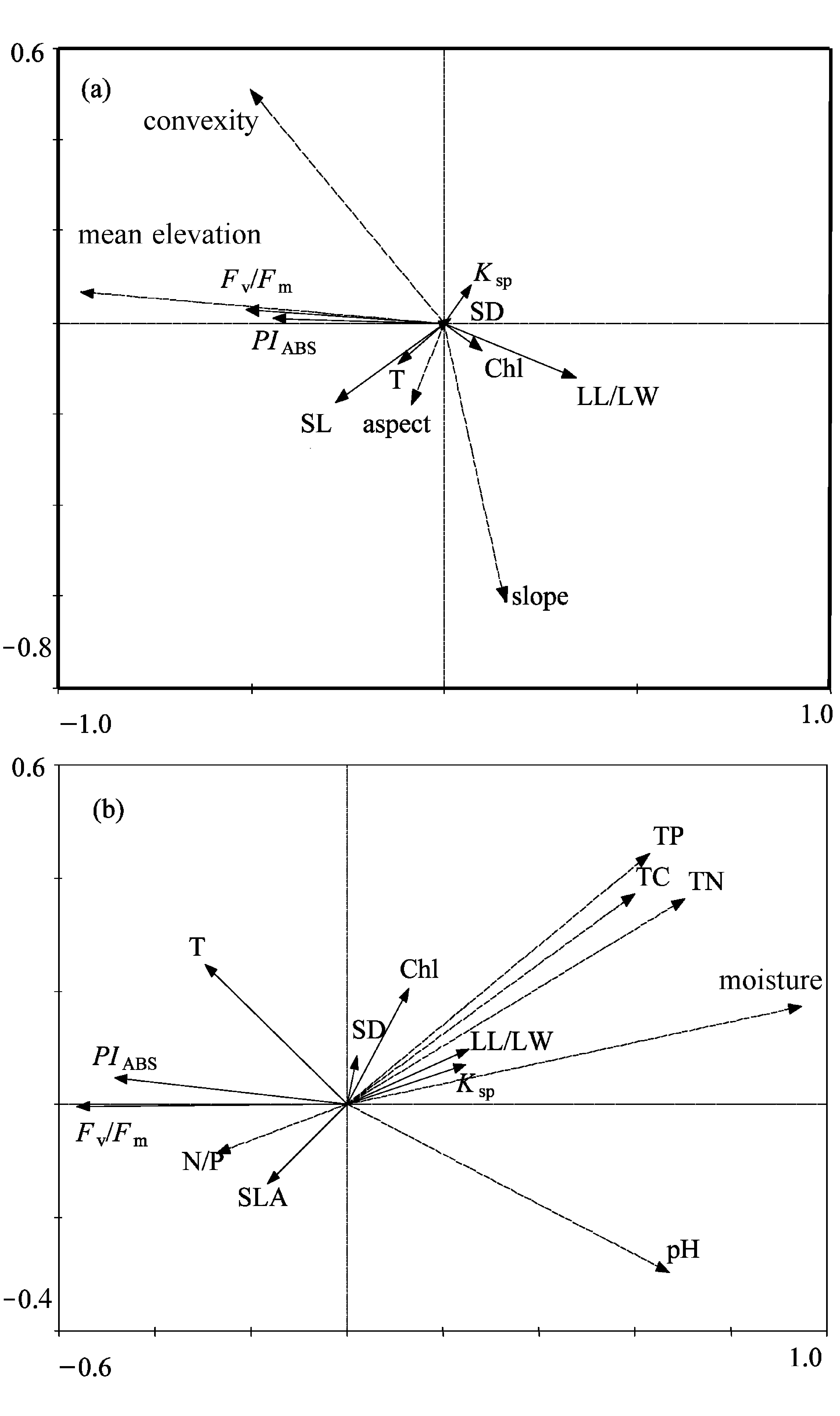
图中实线特征向量表示功能性状, 虚线特征向量表示地形因子,横纵坐标表示负荷量。Chl, 叶绿素含量; Fv/Fm, PSII的最大光化学效率; PIABS, 基于光能吸收的PSII光化学综合性能指数; Ksp, 枝条比导率; SD, 气孔密度; T, 叶片厚度; SLA, 比叶面积; LL/LW, 叶长/宽比; mean elevation, 平均海拔; convexity, 凹凸度; TC, TN, TP, 土壤全碳、全氮、全磷含量; moisture, 土壤含水量; N/P, 土壤氮/磷比。
Functional traits are displayed in solid arrows and topological data in dashed arrows. Chl, Chlorophyll content; Fv/Fm, Maximal photochemical efficiency of photo system II; PIABS, Performance index on basis of light energy absorption; Ksp, Stem sapwood xylem specific hydraulic conductivity; SD, Stomata density; T, Leaf thickness; SLA, Specific leaf area; LL/LW, Ratio of leaf length to leaf width; TP, TC and TN, Content of total soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, respectively; N/P, Ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus.