A curated 16S rRNA reference database for the classification of honeybee and bumblebee gut microbiota
Zhang Xue, Li Xing’an, Su Qinzhi, Cao Qina, Li Chenyi, Niu Qingsheng, Zheng Hao
Biodiv Sci
2019, 27 ( 5):
557-566.
DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019021
Honey and bumble bees are import pollinators, playing significant roles in the agricultural industry and maintaining the bio-ecosystem balance. Recently, it was found that the bees harbor a simple, yet specific gut microbiota. The normal bee gut microbiota makes essential contributions to host growth, endocrine signaling, and pathogen resistance. With the development of high through-put sequencing technology, researchers can now quickly identify the gut community structure for a low cost. This is helpful for biodiversity, conservation and bee health studies. However, the currently-used 16S rRNA databases are not specific enough to classify the bee gut microbiota properly. Many of the specific bacteria that enrich the gut of Apis cerana are in the genus Apibacter. Here, we isolated Apibacter species from A. cerana collected in five provinces of China, and added them to the current SILVA database. We also curated the nomenclature of some existing sequences and re-classified them in the updated database. Based on the analysis of the 16S rRNA sequencing data from one A. cerana and one Apis mellifera sample, our Bee Gut Microbiota-Database (BGM-Db) offers a more accurate classification of bee gut microbiota at a higher resolution than either the SILVA or Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) database.
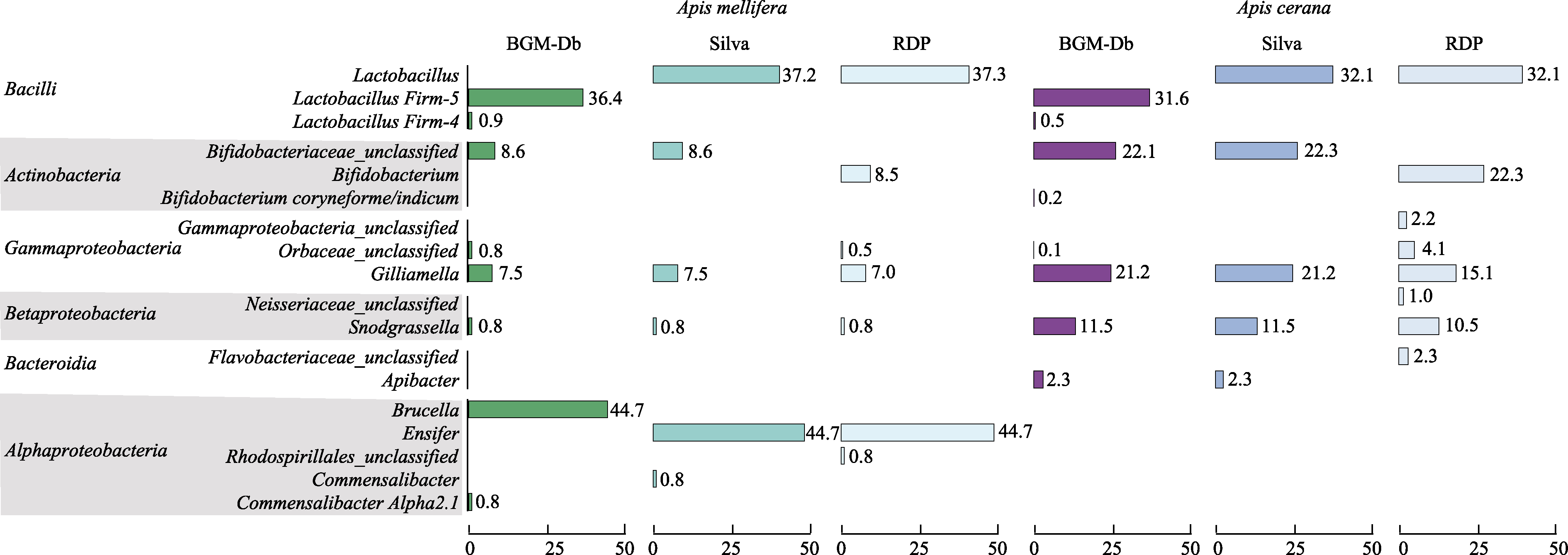
Fig. 2
Comparison of the behaviors of the BGM-Db, SILVA, and Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) databases when they are used in the classification of the gut microbiota of Apis cerana and Apis mellifera
Extracts from the Article
为比较不同16S rRNA数据库在对蜜蜂肠道菌测序结果分类上的差别, 我们分别选取1只西方蜜蜂和1只东方蜜蜂样品, 利用Illumina对其肠道菌16S rRNA扩增结果进行高通量测序, 将测序结果分别利用BGM-Db与已有的SILVA和RDP数据库进行分类(图2)。
提取西方蜜蜂和东方蜜蜂中丰度前10的分类簇, 计算其百分比。其中西方蜜蜂中丰度最高的为α-变形菌, 44%以上的菌种在不同数据库其分类结果有所不同(图2)。BGM-Db将其鉴定为Brucella菌属, 而其他2个数据库则将其分类为Ensifer菌属。Brucella和Ensifer属于Rhizobiales目不同科的菌属, 与西方蜜蜂的核心肠道菌Bartonella属于同一个目。而3个数据库的分类结果均未将其分类到Bartonella属, 甚至Bartonellaceae科, 可能是由于样品测序污染所致, 或者是该西方蜜蜂主要肠道菌与已知的Bartonella进化距离较远, 分化为新的物种, 使其分类到其他科的菌属。另一种α-变形菌, 通过BGM-Db可以将其分类到菌种水平, 为蜜蜂肠道菌Commensalibacter Alpha-2.1; 而SILVA数据库只能将其分类到Commensalibacter属, RDP数据库则只能将其分类到Rhodospirillales科。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|

