



Biodiv Sci ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 593-600. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08121
Special Issue: 土壤生物与土壤健康
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fei Zhao, Xiafang Sheng, Zhi Huang, Linyan He( )
)
Received:2008-05-27
Accepted:2008-10-27
Online:2008-11-20
Published:2008-11-20
Contact:
Linyan He
About author:* E-mail: helyan0794@njau.edu.cnFei Zhao, Xiafang Sheng, Zhi Huang, Linyan He. Isolation of mineral potassium-solubilizing bacterial strains from agricultural soils in Shandong Province[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(6): 593-600.
| 菌株 Strains | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 土壤类型 Soil type | 植物种类 Plants | 代谢产物 Metabolism products | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吲哚乙酸 IAA | 铁载体 Sidersphore | ||||
| AC2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 无 Bulk | + + | + + |
| ACY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | + + |
| ACM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
| ACG2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + + | – |
| ACD2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 大豆 Soybean | + | + + |
| ACZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| ACY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| ACZ3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | – |
| AZZ4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AZH4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 红薯 Sweet potato | + | + |
| AZZ5 | 威海 Weihai City | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AHY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| AHZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | + + |
| ASY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + + |
| ASG1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + | + + |
| ASZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | – |
| AZY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 玉米 Maize | ++ | + |
| AZZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 杂草 Weeds | + | + |
| AF2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 无 Bulk | + | – |
| AFM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 棉花 Cotton | + + | – |
| AFY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + |
| AY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 无 Bulk | + | + + |
| AYM3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
Table 1 Indoleacetic acid (IAA) and sidersphore production of isolates obtained from the rhizosphere of various plants in different soils types, Shandong Province
| 菌株 Strains | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 土壤类型 Soil type | 植物种类 Plants | 代谢产物 Metabolism products | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吲哚乙酸 IAA | 铁载体 Sidersphore | ||||
| AC2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 无 Bulk | + + | + + |
| ACY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | + + |
| ACM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
| ACG2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + + | – |
| ACD2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 大豆 Soybean | + | + + |
| ACZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| ACY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| ACZ3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | – |
| AZZ4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AZH4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 红薯 Sweet potato | + | + |
| AZZ5 | 威海 Weihai City | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AHY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| AHZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | + + |
| ASY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + + |
| ASG1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + | + + |
| ASZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | – |
| AZY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 玉米 Maize | ++ | + |
| AZZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 杂草 Weeds | + | + |
| AF2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 无 Bulk | + | – |
| AFM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 棉花 Cotton | + + | – |
| AFY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + |
| AY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 无 Bulk | + | + + |
| AYM3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
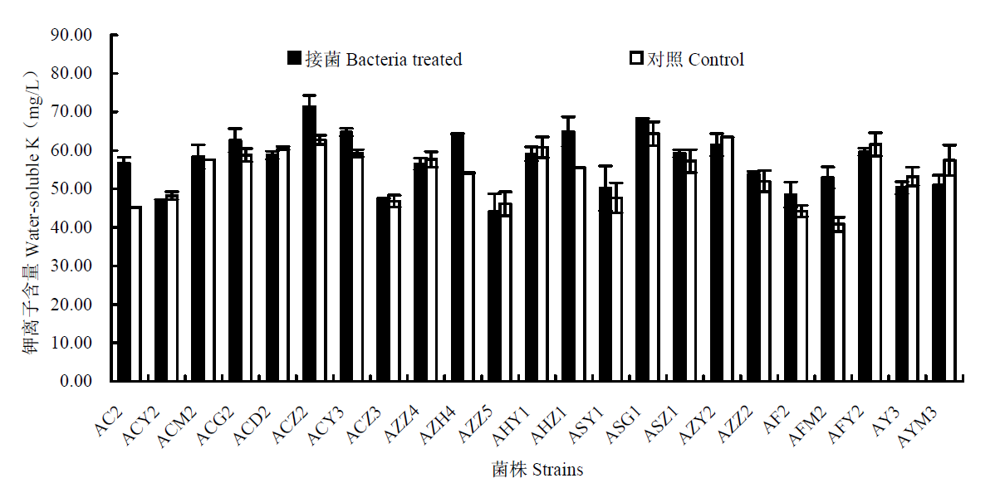
Fig. 1 Amount of potassium (K) released by bacterial strains after four days inoculation in liquid cultures. Controls were inoculated by autoclaved inocula.
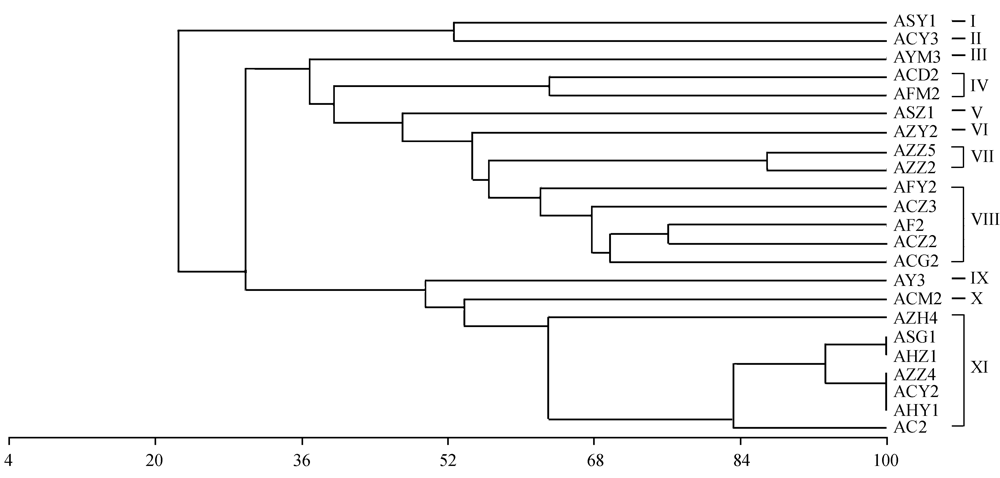
Fig. 2 A UPGMA dendrogram of 23 potassium-releasing bacterial strains based on amplified rDNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) patterns from Hae Ⅲ and MspⅠdigestion.
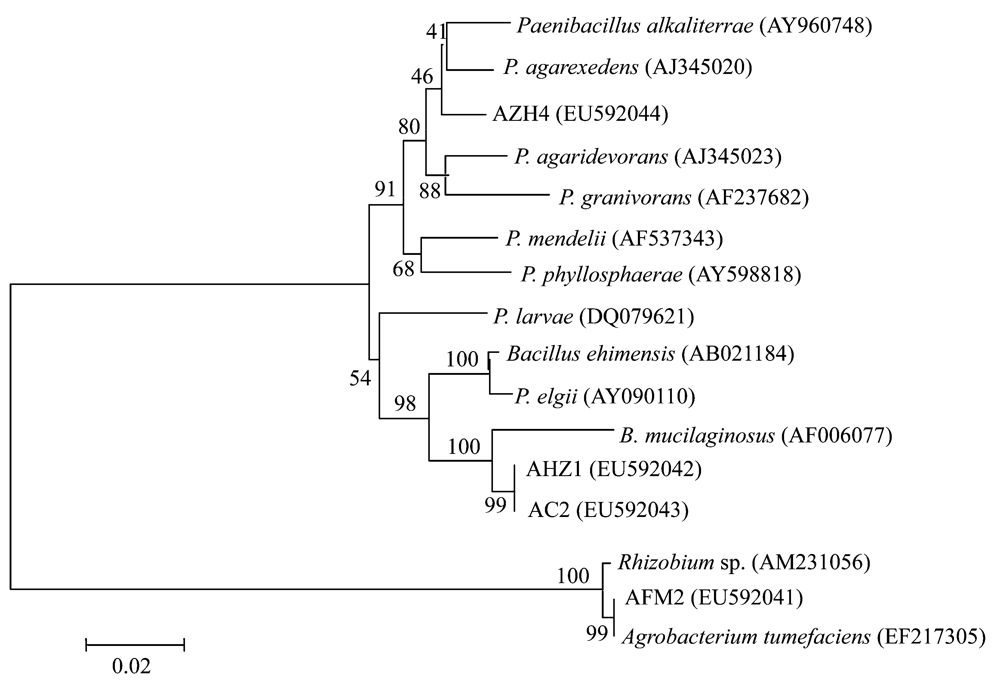
Fig. 3 The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA sequences of four potassium-bearing mineral-dissolved bacteria strains and those of related species in the genusBacillus, Paebacillus, Rhizobium, and Agrobacterium. Scale bar indicates evolutionary distance.
| [1] | Banfield JF, Barker WW, Welch SA, Taunton A (1999) Biological impact on mineral dissolution: application of the lichen model to understanding mineral weathering in the rhizosphere. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 96,3404-3411. |
| [2] | Barker WW, Welch SA, Chu S, Banfield JF (1998) Experimental observations of the effects of bacteria on aluminosilicate weathering. American Mineralogist, 83,1551-1563. |
| [3] | Buss HL, Lüttge A, Brantley SL (2007) Etch pit formation on iron silicate surfaces during siderophore-promoted dissolution. Chemical Geology, 240,326-342. |
| [4] | Calvaruso C, Turpault MP, Frey-Klett P (2006) Root-associated bacteria contribute to mineral weathering and to mineral nutrition in trees: a budgeting analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72,1258-1266. |
| [5] |
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka E (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,4951-4959.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2005) Analysis of rhizobacterial communities in perennial Graminaceae from polluted water meadow soil, and screening of metal-resistant, potentially plant growth-promoting bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 52,153-162.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 41,109-114. |
| [8] | Guan Y (管莹), Li DY (李登煜), Chen Q (陈强), Zhou JC (周俊初), Zhang WT (张伟涛), Jing GJ (荆光军) (2007) Genetic diversity of silicate bacteria isolated from saline-alkali soils in northern China by RAPD and BOXAIR PCR analysis. Journal of Agro-Environment Science (农业环境科学学报), 26,2043-2047. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] |
Hameeda B, Harini G, Rupela OP, Wani SP, Reddy G (2008) Growth promotion of maize by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from composts and macrofauna. Microbiological Research, 163,234-242.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] | He JQ (贺积强), Li DY (李登煜), Zhang XP (张小平), Chen Q (陈强), Liang RY (梁如玉) (2003) Phenotypic aspects and phosphorus-releasing and potassium-releasing ability of silicate bacteria isolated from purple soils. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (应用与环境生物学报), 9,71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | He LY (何琳燕), Sheng XF (盛下放), Lu GX (陆光祥), Huang WY (黄为一) (2004) Physiological and biochemical characteristics of silicate-dissolving bacteria in different soils and their capacities of releasing potassium. Soils (土壤), 36,434-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Hiebert FK, Bennett PC (1992) Microbial control of silicate weathering in organic-rich ground water. Science, 258,278-281.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Hu H (胡桦), Chen Q (陈强), Li DY (李登煜), Wu SS (吴思思), Xie ZL (谢卓霖), He JQ (贺积强), Zhou JC (周俊初) (2007) Genetic diversity of silicate bacteria isolated from purple soils. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 44,379-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Kalinowski BE, Liermann LJ, Brantley SL, Barnes A, Pantano CG (2000) X-ray photoelectron evidence for bacteria-enhanced dissolution of hornblende. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64,1331-1343. |
| [15] |
Laguerre G, Allard M, Revoy F (1994) Rapid identification of rhizobia by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60,56-63.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] | Li DX (李定旭) (2003) Study on the effects of silicate bacteria on the growth and fruit quality of apples. Journal of Fruit Science (果树学报), 20,64-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Li J (李俊), Jiang X (姜昕), Li L (李力), Shen DL (沈德龙) (2006) Development of microbial fertilizer and maintaining of soil biological fertility. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (中国土壤与肥料), (4),1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Li S (李莎), Li FC (李福春), Cheng LJ (程良娟) (2006) Recent development in bio -weathering research. Mineral Resources and Geology (矿产与地质), 20,577-582. |
| [19] | Li Y (李扬), Li DY (李登煜), Huang MY (黄明勇), Chen Q (陈强), Zhang XP (张小平), Liu X (刘旭) (2006) Study on biological characteristics of several silicate bacteria isolated from saline soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science (土壤通报), 37,206-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Lian B (连宾), Fu PQ (傅平秋), Mo DM (莫德明), Liu CQ (刘丛强) (2002) A comprehensive review of the mechanism of potassium releasing by silicate bacteria. Acta Mineralogic Sinica (矿物学报), 22,179-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Rogers JR, Bennett PC (2004) Mineral stimulation of subsurface microorganisms: release of limiting nutrients from silicates. Chemical Geology, 203,91-108. |
| [22] | Sambrook J, Maniatis T, Fritsch EF (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York. |
| [23] | Sheng XF (2005) Growth promotion and increased potassium uptake of cotton and rape by a potassium releasing strain of Bacillus edaphicus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37,1918-1922. |
| [24] |
Sheng XF, He LY (2006) Solubilization of potassium-bearing minerals by a wild-type strain of Bacillus edaphicus and its mutants and increased potassium uptake by wheat. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 52,66-72.
URL PMID |
| [25] | Sheng XF (盛下放) (2004) Distribution of silicate-dissolving bacteria in soils of China. Soils (土壤), 36,81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Sheng XF (盛下放), Huang WY(黄为一) (2001) Physiological characteristics of strain NBT of silicate bacterium. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 38,569-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Sheng XF (盛下放), Huang WY (黄为一) (2002) Mechanism of potassium release from feldspar affected by the strain NBT of silicate bacterium. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 39,863-871. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Sheng XF, He LY, Huang WY (2002) The conditions of releasing potassium by a silicate-dissolving bacterial strain NBT. Agricultural Sciences in China, 1,662-666. |
| [29] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24,1596-1599.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Wang P (王平), Dong B (董飙), Li FD (李阜棣), Hu ZJ (胡正嘉) (1994) Detection and determination of the siderophores produced by wheat rhizobacteria. Microbiology (微生物学通报), 21,323-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Zhang SM (张漱茗), Yan H (闫华), Liu GD (刘光栋), Liu ZH (刘兆辉) (1999) Soil potassium supplying capacity and release of non-exchangeable potassium in Shandong soils. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science (植物营养与肥料学报), 5(1),26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Zhu CX (朱昌雄), Li J (李俊), Shen DL (沈德龙), Jiang X (姜昕) (2005) Research progress of bio-fertilizer standardization in China and some suggestions. Phosphate and Compound Fertilizer (磷肥与复肥), 20(4),5-7, 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [2] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [4] | Yuanyuan Xiao, Wei Feng, Yangui Qiao, Yuqing Zhang, Shugao Qin. Effects of soil microbial community characteristics on soil multifunctionality in sand-fixation shrublands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [5] | Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen. Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang. Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [7] | Weiyue Sun, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Morigengaowa, Xiajin Du, Baodong Liu, Yuehong Yan. Conservation genomics analysis revealed the endangered mechanism of Adiantum nelumboides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [8] | Xiaoyan Jiang, Shengjie Gao, Yan Jiang, Yun Tian, Xin Jia, Tianshan Zha. Species diversity, functional diversity, and phylogenetic diversity in plant communities at different phases of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy grassland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [9] | Togtokh Mongke, Dongyi Bai, Tugeqin Bao, Ruoyang Zhao, Tana An, Aertengqimike Tiemuqier, Baoyindeligeer Mongkejargal, Has Soyoltiin, Manglai Dugarjaviin, Haige Han. Assessment of SNPs-based genomic diversity in different populations of Eastern Asian landrace horses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | Jing Cui, Mingfang Xu, Qun Zhang, Yao Li, Xiaoshu Zeng, Sha Li. Differences in genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in the coastal water of China and Japan based on three mitochondrial markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [11] | Xinyu Cai, Xiaowei Mao, Yiqiang Zhao. Methods and research progress on the origin of animal domestication [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21457-. |
| [12] | Jun Sun, Yuyao Song, Yifeng Shi, Jian Zhai, Wenzhuo Yan. Progress of marine biodiversity studies in China seas in the past decade [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [13] | Dongmei Li, Weihong Yang, Qingduo Li, Xi Han, Xiuping Song, Hong Pan, Yun Feng. High prevalence and genetic variation of Bartonella species inhabiting the bats in southwestern Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [14] | Bo Chen, Lan Jiang, Ziyang Xie, Yangdi Li, Jiaxuan Li, Mengjia Li, Chensi Wei, Cong Xing, Jinfu Liu, Zhongsheng He. Taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of plants in a Castanopsis kawakamiinatural forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(4): 439-448. |
| [15] | Zhi Yao, Jun Guo, Chenzhong Jin, Yongbo Liu. Endangered mechanisms for the first-class protected Wild Plants with Extremely Small Populations in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()