



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 174-182. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014243
• 研究报告: 热带亚热带森林大样地群落结构与格局 • 上一篇 下一篇
练琚愉1, 陈灿1,2, 黄忠良1,*( ), 曹洪麟1, 叶万辉1
), 曹洪麟1, 叶万辉1
收稿日期:2014-11-21
接受日期:2015-03-18
出版日期:2015-03-20
发布日期:2015-04-09
通讯作者:
黄忠良
基金资助:
Juyu Lian1, Can Chen1,2, Zhongliang Huang1,*( ), Honglin Cao1, Wanhui Ye1
), Honglin Cao1, Wanhui Ye1
Received:2014-11-21
Accepted:2015-03-18
Online:2015-03-20
Published:2015-04-09
Contact:
Huang Zhongliang
摘要:
研究不同成熟度群落物种的共存状态, 了解群落演替过程中结构的动态变化, 对揭示森林不同发育时期的群落构建机制具有重要意义。本研究基于鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20 ha固定监测样地(以下简称鼎湖山大样地) 2010年植被调查的数据, 根据径级与林龄将鼎湖山大样地划分为成熟林和过熟林两个斑块, 对其群落物种组成、区系特征及径级结构进行了初步的比较。研究发现: (1)成熟林和过熟林种类组成的群落相似性系数高、物种多样性指数相近, 以及锥栗(Castanopsis chinensis)重要值相似, 但物种数、密度、总胸高断面积、物种重要值等有所不同; (2)热带区系成分在两个斑块均占优势, 但以过熟林的比例较高; (3)两个斑块虽然所有活立木径级结构分布均呈倒“J”型, 但在同径级个体群重要值比较中, 成熟林中径级个体群重要值较高, 而过熟林则是大径级个体群重要值较高。由此可见, 鼎湖山大样地的成熟林与过熟林虽属于同一类群落的演替顶极阶段, 但群落结构上却存在差异, 推测在林窗作用下不同发育时期的群落存在不同的构建过程。
练琚愉, 陈灿, 黄忠良, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉 (2015) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林不同成熟度群落特征的比较. 生物多样性, 23, 174-182. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014243.
Juyu Lian, Can Chen, Zhongliang Huang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye (2015) Community composition and stand age in a subtropical forest, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 174-182. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014243.
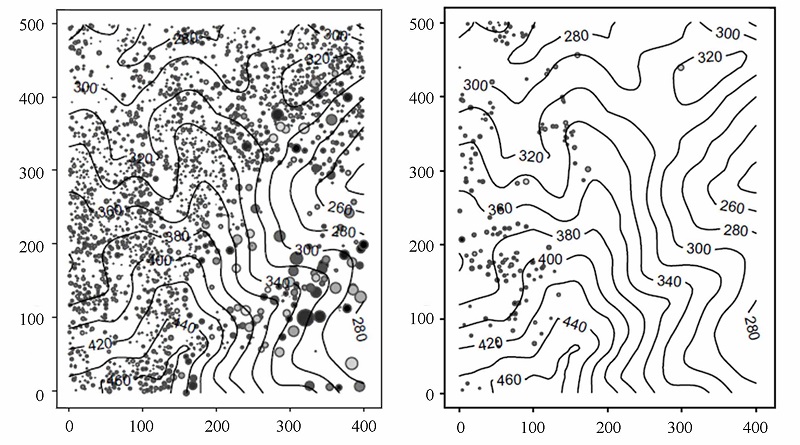
图1 鼎湖山大样地锥栗(左图)和马尾松(右图)胸径≥ 1 cm的个体空间分布图。圆点大小按同等比例表征个体胸径。
Fig. 1 Distribution of Castanopsis chinensis (left) and Pinus massoniana (right) trees (DBH ≥ 1 cm) in the 20 ha Dinghushan plot. Dot size was characterized in equal proportion of individual DBH.
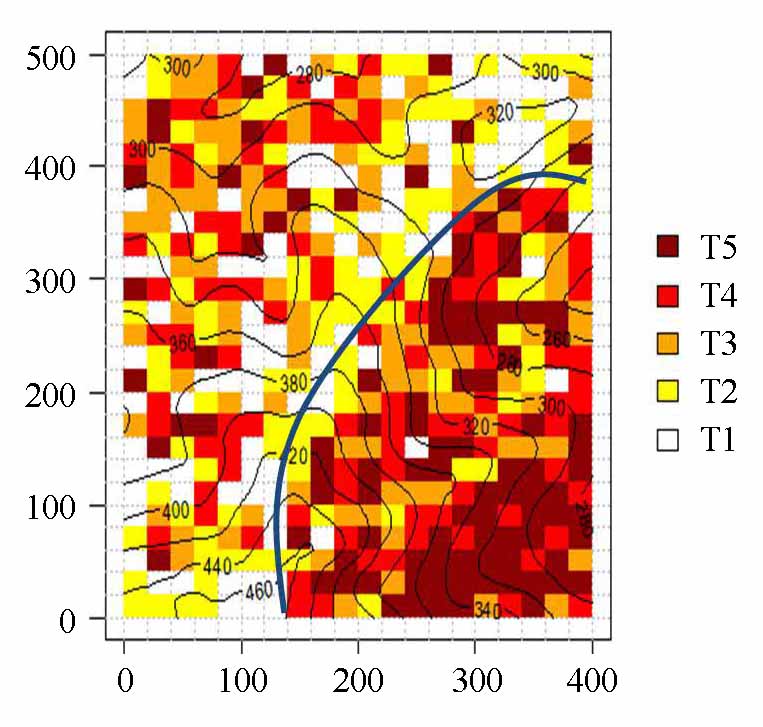
图2 鼎湖山大样地成熟林(蓝线以左)和过熟林(蓝线以右)样地示意图。T1到T5不同的颜色代表小样方的相对年龄, T1最小, T5最大。
Fig. 2 The mature forest (left of blue line) and the old forest (right of blue line) in Dinghushan plot. From the oldest to the youngest: T5, T4, T3, T2, T1.
| 类型 Type | 面积 Area (ha) | 样方数 No. of subplots | 株数 No. of individuals | 植株密度 Density (ind./subplot) | 物种数 No. of species | 群落相似性系数 Chao-Jaccard/Chao-Sorenson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成熟林 Mature forest | 11.8 | 296 | 32,239 | 108.9 ± 40.7 | 141 | 99.07% 99.54% |
| 过熟林 Old forest | 8.2 | 204 | 27,803 | 136.3 ± 52.4 | 157 |
表1 鼎湖山大样地成熟林和过熟林概况
Table 1 Introduction of the mature forest and old forest in the Dinghushan plot
| 类型 Type | 面积 Area (ha) | 样方数 No. of subplots | 株数 No. of individuals | 植株密度 Density (ind./subplot) | 物种数 No. of species | 群落相似性系数 Chao-Jaccard/Chao-Sorenson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成熟林 Mature forest | 11.8 | 296 | 32,239 | 108.9 ± 40.7 | 141 | 99.07% 99.54% |
| 过熟林 Old forest | 8.2 | 204 | 27,803 | 136.3 ± 52.4 | 157 |
| 物种名 Species | 科名 Family | 密度 Density (ind./ha) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m²/ha) | 重要值/排名 Importance value/Ranking | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | OF | MF | OF | MF | OF | ||||
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 151.86 | 34.76 | 9.61 | 7.50 | 14.43/① | 11.00/① | ||
| 荷木 Schima superba | 山茶科 Theaceae | 137.20 | 33.54 | 4.93 | 2.20 | 8.74/② | 3.94/⑥ | ||
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 41.53 | 13.29 | 4.30 | 0.95 | 6.32/③ | 1.75 | ||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 325.85 | 493.90 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 5.53/④ | 6.47/② | ||
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron scleranthum | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 134.15 | 32.93 | 1.86 | 0.46 | 4.92/⑤ | 1.58 | ||
| 黄果厚壳桂 Cryptocarya concinna | 樟科 Lauraceae | 273.81 | 73.17 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 4.69/⑥ | 1.70 | ||
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 148.47 | 63.05 | 1.07 | 1.18 | 4.29/⑦ | 3.00/⑨ | ||
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 167.71 | 380.98 | 0.53 | 1.23 | 3.68/⑧ | 6.47/③ | ||
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 163.31 | 121.95 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 2.78/⑨ | 2.15 | ||
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 102.46 | 233.78 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 2.24/⑩ | 3.49/⑧ | ||
| 小计 Total of above | 1,646.35 | 1,481.35 | 22.72 | 14.13 | 57.62 | 41.55 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1,085.76 | 1,909.26 | 5.7 | 10.87 | 42.38 | 58.45 | |||
| 总计 Total | 2,732.12 | 3,390.61 | 28.4 | 25.0 | 100 | 100 | |||
表2 鼎湖山大样地成熟林重要值前十的物种与过熟林中的比较
Table 2 The top 10 species based on the importance value in the mature forest and old forest of the Dinghushan plot
| 物种名 Species | 科名 Family | 密度 Density (ind./ha) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m²/ha) | 重要值/排名 Importance value/Ranking | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | OF | MF | OF | MF | OF | ||||
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 151.86 | 34.76 | 9.61 | 7.50 | 14.43/① | 11.00/① | ||
| 荷木 Schima superba | 山茶科 Theaceae | 137.20 | 33.54 | 4.93 | 2.20 | 8.74/② | 3.94/⑥ | ||
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 41.53 | 13.29 | 4.30 | 0.95 | 6.32/③ | 1.75 | ||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 325.85 | 493.90 | 0.20 | 0.41 | 5.53/④ | 6.47/② | ||
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron scleranthum | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 134.15 | 32.93 | 1.86 | 0.46 | 4.92/⑤ | 1.58 | ||
| 黄果厚壳桂 Cryptocarya concinna | 樟科 Lauraceae | 273.81 | 73.17 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 4.69/⑥ | 1.70 | ||
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 148.47 | 63.05 | 1.07 | 1.18 | 4.29/⑦ | 3.00/⑨ | ||
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 167.71 | 380.98 | 0.53 | 1.23 | 3.68/⑧ | 6.47/③ | ||
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 163.31 | 121.95 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 2.78/⑨ | 2.15 | ||
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 102.46 | 233.78 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 2.24/⑩ | 3.49/⑧ | ||
| 小计 Total of above | 1,646.35 | 1,481.35 | 22.72 | 14.13 | 57.62 | 41.55 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1,085.76 | 1,909.26 | 5.7 | 10.87 | 42.38 | 58.45 | |||
| 总计 Total | 2,732.12 | 3,390.61 | 28.4 | 25.0 | 100 | 100 | |||
| 类型 Type | Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 成熟林 Mature forest | 2.63 ± 0.28 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.07 |
| 过熟林 Old forest | 2.71 ± 0.29 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.81 ± 0.06 |
表3 鼎湖山大样地成熟林和过熟林物种多样性指数(mean ± SD)
Table 3 Species diversity indices of the mature forest and old forest in the Dinghushan plot (mean ± SD)
| 类型 Type | Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 成熟林 Mature forest | 2.63 ± 0.28 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.07 |
| 过熟林 Old forest | 2.71 ± 0.29 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.81 ± 0.06 |
| 分布区类型 Distribution area type | 成熟林 Mature forest | 过熟林 Old forest | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属数 No. of genera | 比率 Percentage (%) | 属数 No. of genera | 比率 Percentage (%) | ||
| 2 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 31 | 32.63 | 34 | 35.05 | |
| 3 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 5.26 | 4 | 4.12 | |
| 4 旧世界热带分布 Old World Tropic | 15 | 15.79 | 15 | 15.46 | |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical Australasia | 6 | 6.32 | 5 | 5.15 | |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 7 | 7.37 | 6 | 6.19 | |
| 7 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia | 21 | 22.11 | 25 | 25.77 | |
| 热带成分(分布型2-7) Tropical elements | 85 | 89.47 | 89 | 91.75 | |
| 8 北温带分布 North Temperate | 3 | 3.16 | 1 | 1.03 | |
| 9 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 5 | 5.26 | 6 | 6.19 | |
| 14 东亚分布 East Asia | 2 | 2.11 | 1 | 1.03 | |
| 温带成分(分布型8-14) Temperate elements | 10 | 10.53 | 8 | 8.25 | |
| 合计 Total | 95 | 100.00 | 97 | 100.00 | |
表4 成熟林和过熟林木本植物群落种子植物属的分布区类型统计
Table 4 Distribution area types of spermatophyte of woody plant community in the mature forest and old forest
| 分布区类型 Distribution area type | 成熟林 Mature forest | 过熟林 Old forest | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属数 No. of genera | 比率 Percentage (%) | 属数 No. of genera | 比率 Percentage (%) | ||
| 2 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 31 | 32.63 | 34 | 35.05 | |
| 3 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 5.26 | 4 | 4.12 | |
| 4 旧世界热带分布 Old World Tropic | 15 | 15.79 | 15 | 15.46 | |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia and Tropical Australasia | 6 | 6.32 | 5 | 5.15 | |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 7 | 7.37 | 6 | 6.19 | |
| 7 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia | 21 | 22.11 | 25 | 25.77 | |
| 热带成分(分布型2-7) Tropical elements | 85 | 89.47 | 89 | 91.75 | |
| 8 北温带分布 North Temperate | 3 | 3.16 | 1 | 1.03 | |
| 9 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 5 | 5.26 | 6 | 6.19 | |
| 14 东亚分布 East Asia | 2 | 2.11 | 1 | 1.03 | |
| 温带成分(分布型8-14) Temperate elements | 10 | 10.53 | 8 | 8.25 | |
| 合计 Total | 95 | 100.00 | 97 | 100.00 | |
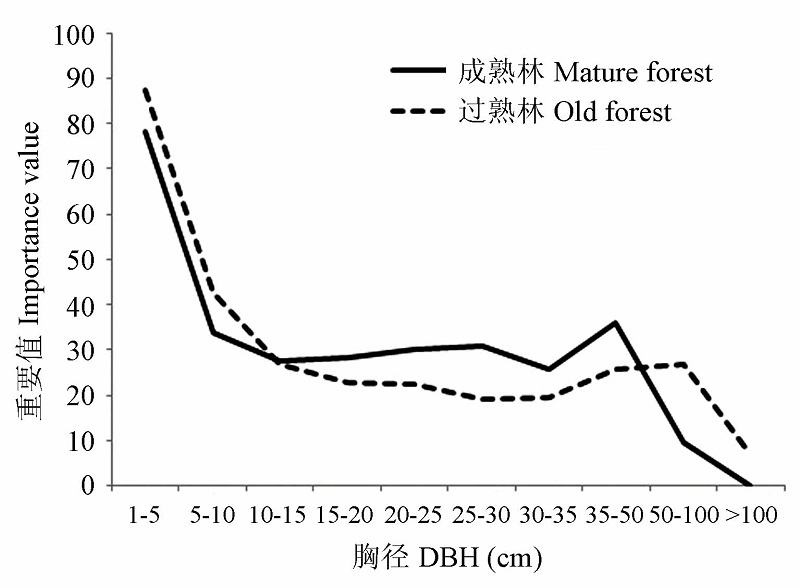
图4 鼎湖山大样地成熟林和过熟林同径级个体群重要值随径级结构的分布
Fig. 4 Importance value of individual groups in the same tree size of the mature forest and old forest in the Dinghushan plot
| 1 | Bruelheide H, Böhnke M, Both S, Fang T, Assmann T, Baruffol M, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fischer M, Geißler C, Guo DL, Guo LD, Härdtle W, He JS, Hector A, Kröber W, Kühn P, Lang AC, Nadrowski K, Pei KQ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Shi XZ, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wu YT, Yang XF, Zeng XQ, Zhang SR, Zhou HZ, Ma KP, Schmid B (2011) Community assembly during secondary forest succession in a Chinese subtropical forest.Ecological Monographs, 81, 25-41. |
| 2 | Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Zhang LY (张林艳) (2002) Vegetation types in Dinghu Mountain Biosphere Reserve.Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem(热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 9, 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Cavender-Bares J, Ackerly DD, Baum DA, Bazzaz FA (2004) Phylogenetic overdispersion in Floridian oak communities.The American Naturalist, 163, 823-843. |
| 4 | Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ (2005) A new statistical approach for assessing similarity of species composition with incidence and abundance data.Ecology Letters, 8, 148-159. |
| 5 | Chazdon RL (2008) Chance and determinism in tropical forest succession. In: Tropical Forest Community Ecology (eds Carson WP, Schnitze SA), pp, 384-408. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford. |
| 6 | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with other Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| 7 | Diamond JM (1975) Assembly of species communities. In: Ecology and Evolution of Communities (eds Cody ML, Diamond JM), pp. 342-444. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| 8 | Gourlet-Fleury S, Beina D, Fayolle A, Ouédraogo DY, Mortier F, Bénédet F, Closset-Kopp D, Decocq G (2013) Silvicultural disturbance has little impact on tree species diversity in a Central African moist forest.Forest Ecology and Management, 304, 322-332. |
| 9 | He JH (何金海), Chen ZQ (陈兆其), Liang YE (梁永奀) (1982) The soil in Dinghu Mountain Biosphere Reserve. Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem(热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 1, 25-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | Houghton JT, Jenkins GJ, Ephraums JJ (1990) Climate Change: the IPCC Scientific Assessment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 11 | Howard LF, Lee TD (2003) Temporal patterns of vascular plant diversity in southeastern New Hampshire forests.Forest Ecology and Management, 185, 5-20. |
| 12 | Huang JH (黄建辉) (1994) The effects of species diversity on the stability of ecosystems. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法) (eds Qian YQ (钱迎倩), Ma KP (马克平)), pp. 178-191. Chinese Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 13 | Huang ZL (黄忠良), Kong GH (孔国辉), Wei P (魏平) (1998) Plant species diversity dynamics in Dinghu Mountain forests.Chinese Biodiversity(生物多样性), 6, 116-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Huang ZL (黄忠良), Kong GH (孔国辉), He DQ (何道泉) (2000) Plant community diversity in Dinghushan Nature Reserve.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 20, 193-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Hubbell SP, Ahumada JA, Condit R, Foster RB (2001) Local neighborhood effects on long-term survival of individual trees in a Neotropical forest.Ecological Research, 16, 859-875. |
| 16 | Jin HJ (靳虎甲), Ma QL (马全林), He MZ (何明珠), Jia XH (贾晓红), Liu YJ (刘有军), Zhang YJ (张有佳), Li FH (李发鸿) (2013) Analysis on community structure and quantitative characteristics of Nitraria tangutorum nebkhas at different succession stage in lower reaches of Shiyang River.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 33, 2248-2259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Kong GH (孔国辉), Ye WH (叶万辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Wei P (魏平), Huang YJ (黄玉佳) (1998) Long-term monitoring of the low subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. I. Species composition of Castanopsis chinensis, Cryptocarya concinna community and its contribution.Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem(热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 8, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 | Liang XD (梁晓东), Ye WH (叶万辉) (2001) Advances in study on forest gaps.Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 9, 355-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Liu YG (刘玉国), Liu CC (刘长成), Wei YF (魏雅芬), Liu YG (刘永刚), Guo K (郭柯) (2011) Species composition and community structure at different vegetation successional stages in Puding, Guizhou Province, China.Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 35, 1009-1018. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Lu ZJ (卢志军), Bao DC (鲍大川), Guo YL (郭屹立), Lu JM (路俊盟), Wang QG (王庆刚), He D (何东), Zhang KH (张奎汉), Xu YZ (徐耀粘), Liu HB (刘海波), Meng HJ (孟红杰), Huang HD (黄汉东), Wei XZ (魏新增), Liao JX (廖建雄), Qiao XJ (乔秀娟), Jiang MX (江明喜), Gu ZR (谷志容), Liao CL (廖春林) (2013) Community composition and structure of Badagongshan (BDGS) Forest Dynamic Plot in a mid-subtropical mountain evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest, Central China.Plant Science Journal(植物科学学报), 31, 336-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Ma KP (马克平), Liu YM (刘玉明) (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2).Chinese Biodiversity(生物多样性), 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| 22 | Manion PD, Lachance D (1992) Forest decline concepts: an overview. In: Forest Decline Concepts (eds Manion PD, Lachance D), pp. 181-190. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul. |
| 23 | Margalef R (1963) On certain unifying principles in ecology.The American Naturalist, 97, 357-374. |
| 24 | Niu HY (牛红玉) (2012) Community Assembly in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest (亚热带常绿阔叶林群落构建特征的研究). PhD dissertation, South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 25 | Odum EP (1971) Fundamentals of Ecology, 3rd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. |
| 26 | Peng SL (彭少麟) (1996) Community Dynamics in Lower Subtropical Forest (南亚热带森林群落动态学). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 27 | Peng SL (彭少麟), Fang W (方炜), Ren H (任海), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Kong GH (孔国辉), Yu QF (余清发), Zhang DQ (张德强) (1998) The dynamics on organization in the successional process of Dinghushan Cryptocarya community. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 22, 245-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 28 | Réjou-Méchain M, Flores O, Pélissier R, Fayolle A, Fauvet N, Gourlet-Fleury S (2014) Tropical tree assembly depends on the interactions between successional and soil filtering processes.Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1440-1449. |
| 29 | Rosenzweig C, Parry ML (1994) Potential impact of climate change on world food supply.Nature, 367, 133-138. |
| 30 | Shang YC (尚玉昌) (2002) General Ecology (普通生态学). Peking University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 31 | Song YC (宋永昌) (2001) Vegetation Ecology (植被生态学). East China Normal University Publishing House, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| 32 | Tilman D, Pacala S (1993) The maintenance of species richness in plant communities. In: Species Diversity in Ecological Communities (eds Ricklefs RE, Schluter D), pp. 13-25. University of Chicago, Chicago. |
| 33 | Wang ZH (王铸豪), He DQ (何道泉), Song SD (宋绍敦), Chen SP (陈树培), Chen DR (陈定如), Tu MZ (屠梦照) (1982) The vegetation of Ding Hu Shan Biosphere Reserve. Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem(热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 1, 77-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plant.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 13(Suppl.), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Yang QS (杨庆松), Ma ZP (马遵平), Xie YB (谢玉彬), Zhang ZG (张志国), Wang ZH (王樟华), Liu HM (刘何铭), Li P (李萍), Zhang N (张娜), Wang DL (王达力), Yang HB (杨海波), Fang XF (方晓峰), Yan ER (阎恩荣), Wang XH (王希华) (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 36 | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China.Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version)(植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Young TP, Chase JM, Huddleston RT (2001) Community succession and assembly: comparing, contrasting, and combining paradigms in the context of ecological restoration. Ecological Restoration, 19, 5-18. |
| 38 | Zhang HD (张宏达), Wang BS (王伯荪), Zhang CC (张超常), Qiu HX (丘华兴) (1955) A study of plant community of Dinghushan in Gaoyao, Guangdong.Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni(中山大学学报 (自然科学版)), 3, 159-225. (in Chinese) |
| 39 | Zhang LY (张林艳), Ye WH (叶万辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良) (2006) Assessment of function area design in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve using landscape ecology principles.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 14, 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 40 | Zhou GS (周广胜), Wang YH (王玉辉) (1999) Research and prospect of global change and climate vegetation classification.Chinese Science Bulletin(科学通报), 44, 2587-2593. (in Chinese) |
| 41 | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [2] | 杨舒涵, 伍一宁, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [3] | 张多鹏, 刘洋, 李正飞, 葛奕豪, 张君倩, 谢志才. 长江上游支流赤水河流域底栖动物物种多样性与保护对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22674-. |
| [4] | 刘彩莲, 许庆, 王林龙, 邢衍阔, 宋稼豪, 林柏岸, 康斌, 刘敏. 闽东近海春秋季游泳动物多样性、密度及群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22635-. |
| [5] | 杨胜娴, 杨清, 李晓东, 巢欣, 刘惠秋, 魏蓝若雪, 巴桑. 确定性过程主导高原典型河流浮游植物地理分布格局和群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [6] | 朱晓华, 高程, 王聪, 赵鹏. 尿素对土壤细菌与真菌多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22636-. |
| [7] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [8] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [9] | 张鹤露, 赵美红, 孙世春, 刘晓收. 西藏那曲市高原盐湖自由生活线虫群落多样性与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22533-. |
| [10] | 魏庐潞, 徐婷婷, 李媛媛, 艾喆, 马飞. 同质园环境和遗传分化影响锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22477-. |
| [11] | 林魏巍, 田呈明, 熊典广, 刘伟航, 热依汗古丽·斯地克, 梁英梅. 新疆杨树人工林中蜘蛛群落多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22493-. |
| [12] | 赵雯, 王丹丹, 热依拉·木民, 黄开钏, 刘顺, 崔宝凯. 阿尔山地区兴安落叶松林土壤微生物群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [13] | 张伟, 翟东东, 熊飞, 刘红艳, 陈元元, 王莹, 廖传松, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 邓华堂, 陈大庆. 三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| [14] | 杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明. 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22492-. |
| [15] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn