



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 568-578. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09140
所属专题: 群落中的物种多样性:格局与机制
收稿日期:2009-06-03
接受日期:2009-11-12
出版日期:2009-11-20
发布日期:2009-11-20
通讯作者:
王襄平
作者简介:*E-mail: wangxiangping@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiangping Wang1,2,*( ), Jingyun Fang1, Zhiyao Tang1
), Jingyun Fang1, Zhiyao Tang1
Received:2009-06-03
Accepted:2009-11-12
Online:2009-11-20
Published:2009-11-20
Contact:
Xiangping Wang
摘要:
物种多样性的地理格局是宏观生态学和生物地理学的核心问题之一, 中域效应假说是该领域的一项重要的理论进展。中域效应是指由于边界对物种分布构成限制, 使不同物种分布区在区域中间重叠程度较大, 而在边界附近重叠较少, 从而形成物种丰富度从边界向中心逐渐增加的格局。现有研究表明, 中域效应是影响物种丰富度格局的一种重要机制, 但其作用大小受很多因素的影响。本文介绍该假说的基本假设和模型, 模拟分析不同模型之间的差异, 并就中域效应假说所展开的争论进行综述, 指出该假说的合理性和局限性。我们认为, 中域效应假说的重要性在于揭示了几何(边界)限制和随机过程在物种多样性地理格局中的作用, 但其目前的模型和假设还过于简单, 需要在深入理解物种分布机制的基础上进行完善和发展。
王襄平, 方精云, 唐志尧 (2009) 中域效应假说: 模型、证据和局限性. 生物多样性, 17, 568-578. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09140.
Xiangping Wang, Jingyun Fang, Zhiyao Tang (2009) The mid-domain effect hypothesis: models, evidence and limitations. Biodiversity Science, 17, 568-578. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09140.
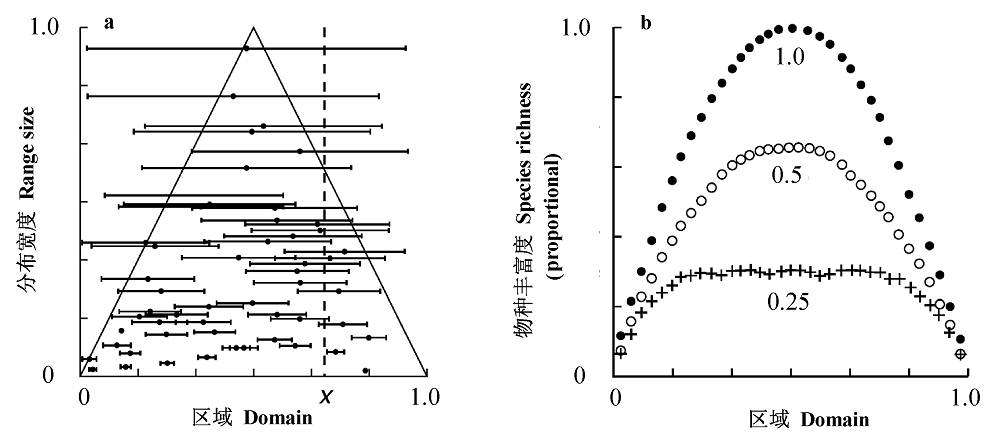
图1 中域效应假说示意图, 横坐标上0和1.0分别代表区域两端的边界。a: 在“物种分布区不超出边界”的假设限制下, 物种分布宽度和中心点之间的关系(中心点只能分布于三角形内), 图中横线段表示各物种的分布区, 其中点为物种中心点。b: 双随机模型模拟的物种丰富度格局(纵坐标为物种数占区域总物种数的比例), 及最大分布宽度限制对模拟结果的影响, 物种的最大分布宽度分别取区域宽度的0.25、0.5 和1.0 (引自Colwell & Lees, 2000)。
Fig. 1 The mid-domain hypothesis for species richness gradients within a bounded domain, the boundaries are denoted by 0 and 1 on the x axis. a, All midpoint-range coordinate pairs must lie within the isosceles triangle under the assumption that species should be distributed within the boundaries. The ranges for species are shown as horizontal lines centered on their midpoints. b, Patterns of species richness across the domain when maximum range size is set to be 0.25, 0.5 and 1.0 of the domain width in the bivariate model. Note that richness is scaled as the proportion of all species in the simulation (from Colwell & Lees, 2000).
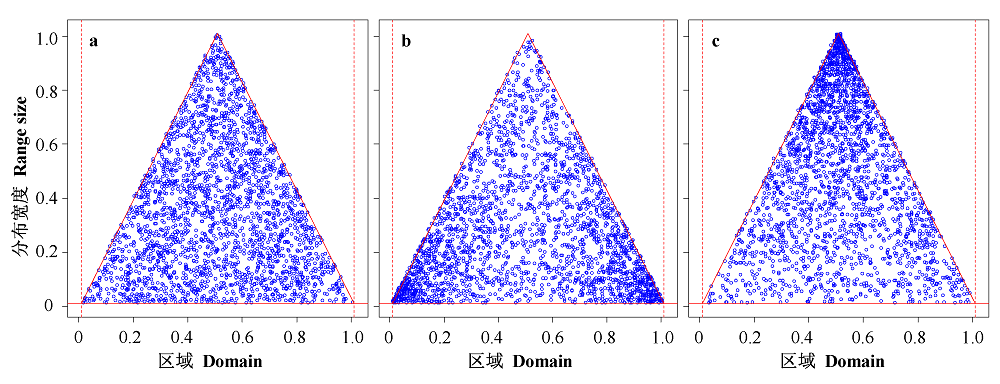
图2 不同中域效应模型产生的物种分布宽度和中心点关系差异。a: 双随机模型; b: 中心点随机模型; c: 分布宽度随机模型。横坐标上0和1.0分别代表区域两端的边界, 因此纵坐标的两端也为0和1.0 (物种分布宽度不能大于区域宽度)。
Fig. 2 Patterns of midpoint-range pairs generated by different mid-domain models. a, the bivariate random model; b, the random midpoint model; c, the random range model. The domain boundaries are denoted by 0 and 1.0 on the x axis, and thus the range of the y axis is also between 0 and 1.0 (the species ranges can not be wider than the domain range because of the geometric constraints).
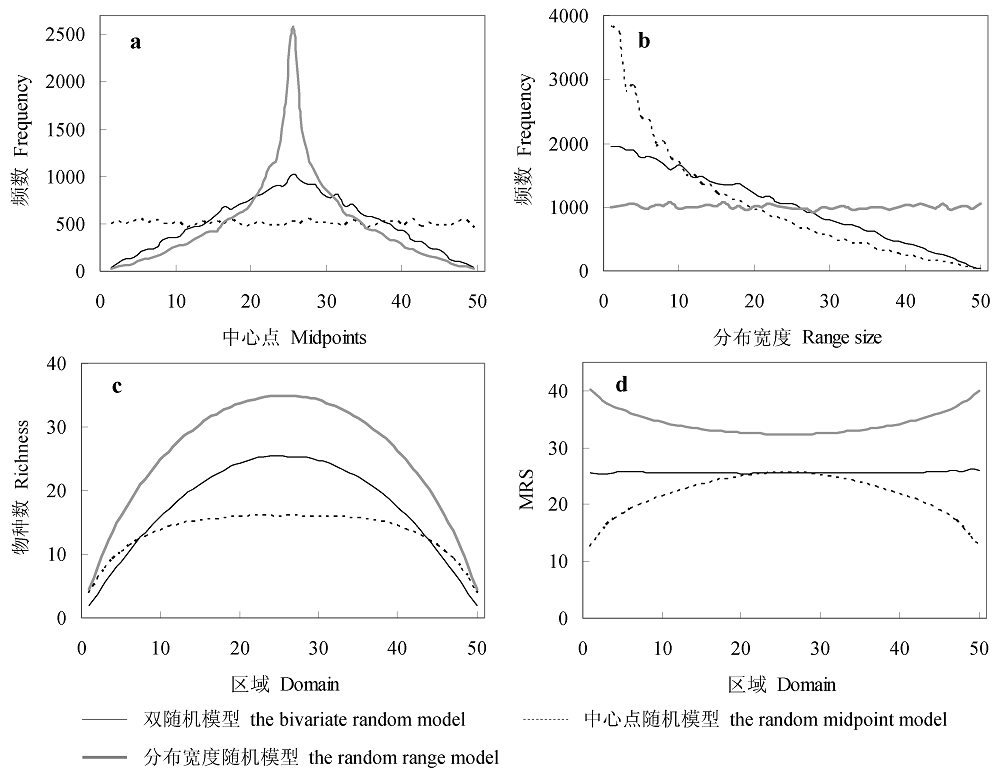
图3 不同中域效应模型模拟结果的差异。a: 物种中心点的频度分布; b: 物种分布宽度的频度分布; c: 物种丰富度格局; d:平均物种分布宽度(MRS)格局。模拟中使用的参数: 总物种数为50, 区域宽度划分为50段, 图中物种丰富度和MRS为1,000次运算的平均值。
Fig. 3 Comparison of patterns generated by different mid-domain models. a, midpoint frequency distribution; b, range size frequency distribution; c, species richness; d, mean range size (MRS). Each simulation was run with 50 species and 50 bins. Species richness and MRS were the means of 1,000 iterations.
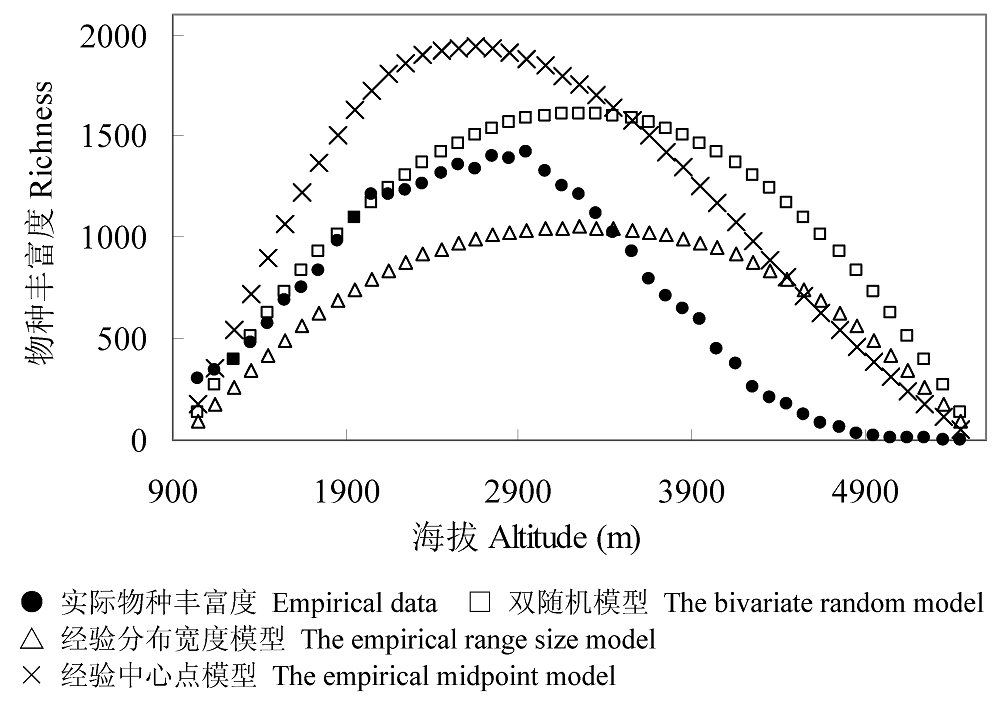
图4 云南丽江地区物种丰富度的垂直格局及不同中域效应模型的模拟结果。物种数据来自吕正伟(1998), 模型的预测值均为500次运算的平均值。
Fig. 4 Altitudinal patterns of species richness in Lijiang region in comparison with patterns simulated by different mid-domain models. The species data were compiled from Lü (1998). The model predictions were the means of 500 iterations.
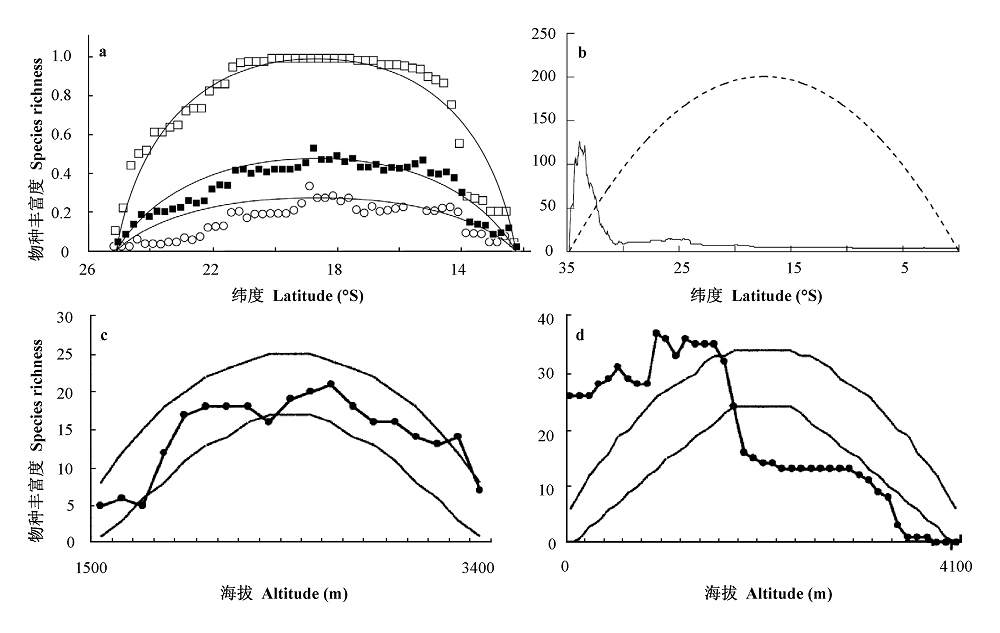
图5 物种丰富度沿纬度和海拔梯度的变化, 每个梯度各举一个符合和偏离中域效应预测的例子, 图a和c与中域效应预测值一致, 而图b和d则不符。a: 马达加斯加岛10类动物物种丰富度的纬度格局, ■ 所有物种, □ 分布区宽的物种, ○ 分布区窄的物种, 实线为中域效应预测值, 纵坐标为物种丰富度占用于模拟的总物种数的比例(Colwell & Lees, 2000)。b: 非洲Cape植物区的山龙眼科物种丰富度的纬度格局, 实线为物种丰富度, 虚线为中域效应预测值(Laurie & Silander, 2002)。c: 美国Aquarius山区小型哺乳动物的物种丰富度垂直格局(McCain, 2005); d: 婆罗洲Kinabalu山小型哺乳动物的物种丰富度格局(McCain, 2005)。图c、d中给出了中域效应预测值的95%置信区间(无数据点的曲线)。
Fig. 5 Empirical patterns of species richness along latitude or altitude gradients. Two of them were consistent with mid-domain model predictions (a and c), while the other two showed remarkable deviation. a, Latitudinal richness pattern for ten faunal groups in Madagascar. ■ Richness pattern for all species; □ Large ranged species; ○ Small ranged species; solid lines, model predictions (Colwell & Lees, 2000). b, Latitudinal richness pattern for Proteaceae in the Cape Floristic Region of Africa. Solid line, observed pattern; dashed line, model prediction (Laurie & Silander, 2002). c, Altitudinal richness patterns of small mammals in Aquarius Mountains of USA. d, Richness patterns of small mammals in Mt. Kinabalu, Borneo. Lines without data points were the 95% confidence limits of mid-domain model predictions (McCain, 2005).
| [1] |
Arita HT (2005) Range size in mid-domain models of species diversity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 232, 119-126.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Bachman S, Baker WJ, Brummitt N, Dransfield J, Moat J (2004) Elevational gradients, area and tropical island diversity: an example from the palms of New Guinea. Ecography, 27, 299-310. |
| [3] | Brown JH (2001) Mammals on mountainsides: elevational patterns of diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 101-109. |
| [4] | Cardelus CL, Colwell RK, Watkins JE (2006) Vascular epiphyte distribution patterns: explaining the mid-elevation richness peak. Journal of Ecology, 94, 144-156. |
| [5] | Colwell RK (2008) RangeModel: tools for exploring and assessing geometric constraints on species richness (the mid-domain effect) along transects. Ecography, 31, 4-7. |
| [6] | Colwell RK, Hurtt GC (1994) Nonbiological gradients in species richness and a spurious Rapoport effect. The American Naturalist, 144, 570-595. |
| [7] |
Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15, 70-76.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Colwell RK, Rahbek C, Gotelli NJ (2004) The mid-domain effect and species richness patterns: what have we learned so far? The American Naturalist, 163, E1-E23.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Colwell RK, Rahbek C, Gotelli NJ (2005) The mid-domain effect: there’s a baby in the bathwater. The American Naturalist, 166, E149-E154. |
| [10] | Currie DJ, Kerr JT (2008) Tests of the mid-domain hypothesis: a review of the evidence. Ecological Monographs, 78, 2-18. |
| [11] | Dunn RR, Colwell RK, Nilsson C (2006a) The river domain: why are there more species halfway up the river? Ecography, 29, 251-259. |
| [12] | Dunn RR, McCain CM, Sanders NJ (2006b) When does diversity fit null model predictions? Scale and range size mediate the mid-domain effect. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 305-312. |
| [13] | Feng JM (冯建孟), Wang XP (王襄平), Li J (李晶), Fang JY (方精云) (2006) Effects of area and mid-domain effect on altitudinal pattern of seed plants richness in Lijiang, Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14, 107-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Fu C, Hua X, Li J, Chang Z, Pu Z, Chen J (2006) Elevational patterns of frog species richness and endemic richness in the Hengduan Mountains, China: geometric constraints, area and climate effects. Ecography, 29, 919-927. |
| [15] |
Gaston KJ (2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature, 405, 220-227.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Gotelli NJ, Graves GR (1996) Null Models in Ecology. Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC. |
| [17] | Grytnes JA, Beaman JH, Romdal TS, Rahbek C (2008) The mid-domain effect matters: simulation analyses of range-size distribution data from Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 2138-2147. |
| [18] | Grytnes JA (2003) Ecological interpretations of the mid-domain effect. Ecology Letters, 6, 883-888. |
| [19] | Hausdorf B (2006) Latitudinal and altitudinal diversity patterns and Rapoport effects in north-west European land snails and their causes. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 87, 309-323. |
| [20] | Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF (2002) The mid-domain effect cannot explain the diversity gradient of Nearctic birds. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 11, 419-426. |
| [21] |
Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF, Weis AE (2005) The mid-domain effect and diversity gradients: is there anything to learn? The American Naturalist, 166, E140-E143.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | He JS (贺金生), Chen WL (陈伟烈) (1997) A review of gradient changes in species diversity of land plant communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 17, 91-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [24] | Jetz W, Rahbek C (2001) Geometric constraints explain much of the species richness pattern in African birds. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 98, 5661-5666. |
| [25] |
Jetz W, Rahbek C (2002) Geographic range size and determinants of avian species richness. Science, 297, 1548-1551.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
Kerr JT, Perring M, Currie DJ (2006) The missing Madagascan mid-domain effect. Ecology Letters, 9, 149-159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Koleff P, Gaston KJ (2001) Latitudinal gradients in diversity: real patterns and random models. Ecography, 24, 341-351. |
| [28] | Krystufek B, Griffiths HI (2002) Species richness and rarity in European rodents. Ecography, 25, 120-128. |
| [29] | Laurie H, Silander JA (2002) Geometric constraints and spatial pattern of species richness: critique of range-based null models. Diversity and Distributions, 8, 351-364. |
| [30] | Lees DC, Kremen C, Andriamampianina L (1999) A null model for species richness gradients: bounded range overlap of butterflies and other rainforest endemics in Madagascar. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 67, 529-584. |
| [31] | Lomolino MV (2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 3-13. |
| [32] | Lü ZW (吕正伟) (1998) Flora of High Mountain Garden and Seed Plants in Lijiang (丽江地区高山园林与种子植物名录). Ethnic Press of Yunnan, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [33] | Lusk CH, Chazdon RL, Hofmann G (2006) A bounded null model explains juvenile tree community structure along light availability gradients in a temperate rain forest. Oikos, 112, 131-137. |
| [34] | Lyons SK, Willig MR (1997) Latitudinal patterns of range size: methodological concerns and empirical evaluations for New World bats and marsupials. Oikos, 79, 568-580. |
| [35] | Lyons SK, Willig MR (1999) A hemispheric assessment of scale-dependence in latitudinal gradients of species richness. Ecology, 80, 2483-2491. |
| [36] | MacArthur RH (1957) On the relative abundance of bird species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 43, 293-295. |
| [37] | McCain CM (2003) North American desert rodents: a test of the mid-domain effect in species richness. Journal of Mammalogy, 84, 967-980. |
| [38] | McCain CM (2004) The mid-domain effect applied to elevational gradients: species richness of small mammals in Costa Rica. Journal of Biogeography, 31, 19-31. |
| [39] | McCain CM (2005) Elevational gradients in diversity of small mammals. Ecology, 86, 366-372. |
| [40] | McCain CM (2007) Could temperature and water availability drive elevational species richness patterns? A global case study for bats. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 1-13. |
| [41] | McClain CR, Etter RJ (2005) Mid-domain models as predictors of species diversity patterns: bathymetric diversity gradients in the deep sea. Oikos, 109, 555-566. |
| [42] | McClain CR, White EP, Hurlbert AH (2007) Challenges in the application of geometric constraint models. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 257-264. |
| [43] | Molles MC (2008) Ecology: Concepts and Applications. McGraw-Hill, New York. |
| [44] | Mora C, Robertson DR (2005) Causes of latitudinal gradients in species richness: a test with fishes of the tropical eastern pacific. Ecology, 86, 1771-1782. |
| [45] |
Morales MA, Dodge GJ, Inouye DW (2005) A phenological mid-domain effect in flowering diversity. Oecologia, 142, 83-89.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
Nogués-Bravo D, Araújo MB, Romdal T, Rahbek C (2008) Scale effects and human impact on the elevational species richness gradients. Nature, 453, 216-220.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] | O’Brien EM (2006) Biological relativity to water-energy dynamics. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1868-1888. |
| [48] | Oommen MA, Shanker K (2005) Elevational species richness patterns emerge from multiple local mechanisms in Himalayan woody plants. Ecology, 86, 3039-3047. |
| [49] | Pineda J, Caswell H (1998) Bathymetric species-diversity patterns and boundary constraints on vertical range distributions. Deep-Sea Research II, 45, 83-101. |
| [50] | Rahbek C (1995) The elevational gradient of species richness: a uniform pattern? Ecography, 18, 200-205. |
| [51] |
Rahbek C (1997) The relationship among area, elevation, and regional species richness in Neotropical birds. The American Naturalist, 149, 875-902.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] | Rahbek C (2005) The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns. Ecology Letters, 8, 224-239. |
| [53] | Rahbek C, Gotelli NJ, Colwell RK, Entsminger GL, Rangel TFLVB, Graves GR (2007) Predicting continental-scale patterns of bird species richness with spatially explicit models. Proceedings of the Royal Society (B), 274, 165-174. |
| [54] | Ribas CR, Schoereder JH (2006) Is the Rapoport effect widespread? Null models revisited. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15, 614-624. |
| [55] | Sandel BS, McKone MJ (2006) Reconsidering null models of diversity: do geometric constraints on species ranges necessarily cause a mid-domain effect? Diversity and Distributions, 12, 467-474. |
| [56] | Sanders NJ (2002) Elevational gradients in ant species richness: area, geometry, and Rapoport’s rule. Ecography, 25, 25-32. |
| [57] | Smith KF, Brown JH (2002) Patterns of diversity, depth range and body size among pelagic fishes along a gradient of depth. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 11, 313-322. |
| [58] | Stevens GC (1989) The latitudinal gradient in geographical range: how so many species coexist in the tropics. The American Naturalist, 133, 240-256. |
| [59] |
Stevens GC (1992) The elevational gradient in altitudinal range: an extension of Rapoport’s latitudinal rule to altitude. The American Naturalist, 140, 893-911.
DOI URL PMID |
| [60] | Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云) (2004) A review on the elevational patterns of plant species diversity. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12, 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] | Tang ZY (唐志尧), Wang ZH (王志恒), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) Historical hypothesis in explaining spatial patterns of species richness. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 635-643. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Tiwari M, Bjorndal KA, Bolten AB, Bolker BM (2005) Intraspecific application of the mid-domain effect model: spatial and temporal nest distributions of green turtles, Chelonia mydas, at Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Ecology Letters, 8, 918-924. |
| [63] | VanDerWal J, Murphy HT, Lovett-Doust J (2008) Three- dimensional mid-domain predictions: geometric constraints in North American amphibian, bird, mammal and tree species richness patterns. Ecography, 31, 435-449. |
| [64] | Wang XH (王希华) (2006) Phytogeography and Species Diversity of Typical Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in China (中国典型常绿阔叶林植物地理与物种多样性研究). PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Wang XP (王襄平) (2008) Altitudinal Patterns of Seed Plant Richness in Mountains Across East China (中国东部山地种子植物γ多样性的垂直格局). Postdoctoral report, Peking University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [66] | Wang Z, Tang Z, Fang J (2007) Altitudinal patterns of seed plant richness in the Gaoligong Mountains, south-east Tibet, China. Diversity and Distributions, 13, 845-854. |
| [67] | Wang ZH (王志恒), Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) The species-energy hypothesis as a mechanism for species richness patterns. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 613-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [68] | Willig MR, Lyons SK (1998) An analytical model of latitudinal gradients of species richness with an empirical test for marsupials and bats in the New World. Oikos, 81, 93-98. |
| [69] | Zapata FA, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2003) Mid-domain models of species richness gradients: assumptions, methods and evidence. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 677-690. |
| [70] |
Zapata FA, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2005) The mid-domain effect revisited. The American Naturalist, 166, E144-E148.
DOI URL PMID |
| [71] | Zhou SR (周淑荣), Zhang DY (张大勇) (2006) Neutral theory in community ecology. Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 30, 868-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [2] | 付裕, 黄康祥, 蔡锦枫, 陈慧敏, 任久生, 万松泽, 张扬, 任珩, 毛瑢, 石福习. 三江平原沼泽湿地4种优势植物空间格局对不同水位环境的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21392-. |
| [3] | 郭英荣, 兰文军, 邹思成, 袁荣斌, 董晓雨, 曹吉锐, 杨清培, 宋庆妮. 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区林下鸟类和兽类资源的红外相机监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 811-818. |
| [4] | 徐翔, 张化永, 谢婷, 孙青青, 田永兰. 西双版纳种子植物物种多样性的垂直格局及机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(7): 678-689. |
| [5] | 郑智, 龚大洁, 孙呈祥, 李晓军, 李万江. 秦岭两栖、爬行动物物种多样性海拔分布格局及其解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 596-607. |
| [6] | 李巧燕, 王襄平. 长江三峡库区物种多样性的垂直分布格局: 气候、几何限制、面积及地形异质性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 141-152. |
| [7] | 林鑫, 王志恒, 唐志尧, 赵淑清, 方精云. 中国陆栖哺乳动物物种丰富度的地理格局及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 652-663. |
| [8] | 卢绮妍, 沈泽昊. 神农架海拔梯度上的植物种域分布特征及Rapoport法则检验[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 644-651. |
| [9] | 张有瑜, 周立志, 王岐山, 王新建, 邢雅俊. 安徽省繁殖鸟类分布格局和热点区分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(3): 305-312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn