



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (3): 263-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07362
收稿日期:2007-12-03
接受日期:2008-02-15
出版日期:2008-05-20
发布日期:2008-05-20
通讯作者:
李建强
作者简介:*E-mail:lijq@rose.whiob.ac.cn
Juan Yan1,2, Haijia Chu1,2, Hengchang Wang1, Jianqiang Li1,*( )
)
Received:2007-12-03
Accepted:2008-02-15
Online:2008-05-20
Published:2008-05-20
Contact:
Jianqiang Li
About author:First author contact:**Contributed equally to this work
摘要:
天蓝苜蓿(Medicago lupulina)隶属于苜蓿属, 是一年生或越年生、广布的草本植物。通常认为它是自交种, 但也有些研究报道它具有异交或者混合交配的繁育系统。为了了解它的居群遗传变异、基因流、繁育方式及其遗传背景, 我们用9个EST-SSR标记分析了中国新疆、内蒙古、甘肃、北京、山西、陕西、湖北7个省区的17个天蓝苜蓿野生居群。结果表明: (1) EST-SSR的多态位点百分率(PPL)为71.9%; 每个SSR位点的等位基因数(A)为4-11(平均为7.333); 遗传多样性(HE)最高的居群是新疆那拉提(0.388), 最低的为陕西西安(0.042)。自交率达93.8%。(2)居群间的遗传分化水平高(FST= 0.528;RST = 0.499), AMOVA分析结果显示遗传变异主要存在于居群间, 占总变异的59.02%。(3) Mantel检验发现遗传距离和地理距离有显著的相关性(r = 0.4141, P ≤ 0.0003)。根据Nei’s遗传距离( Da)得出的Neighbor-joining树显示, 地理距离近的居群聚在一起, 这进一步验证了Mantel检验的结果。由此推测, 天蓝苜蓿中等水平的遗传多样性和高度的居群间遗传分化主要受它的自交特性和分布方式影响。上述结果有助于初步了解天蓝苜蓿的种群动态和遗传结构, 同时对苜蓿属种质资源的保护和遗传育种有重要意义。
闫娟, 楚海家, 王恒昌, 李建强 (2008) 用EST-SSR标记分析中国北部和中部地区天蓝苜蓿的遗传多样性和遗传结构. 生物多样性, 16, 263-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07362.
Juan Yan, Haijia Chu, Hengchang Wang, Jianqiang Li (2008) Genetic structure and diversity of Medicago lupulina populations in northern and central China based on EST-SSRs markers. Biodiversity Science, 16, 263-270. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07362.
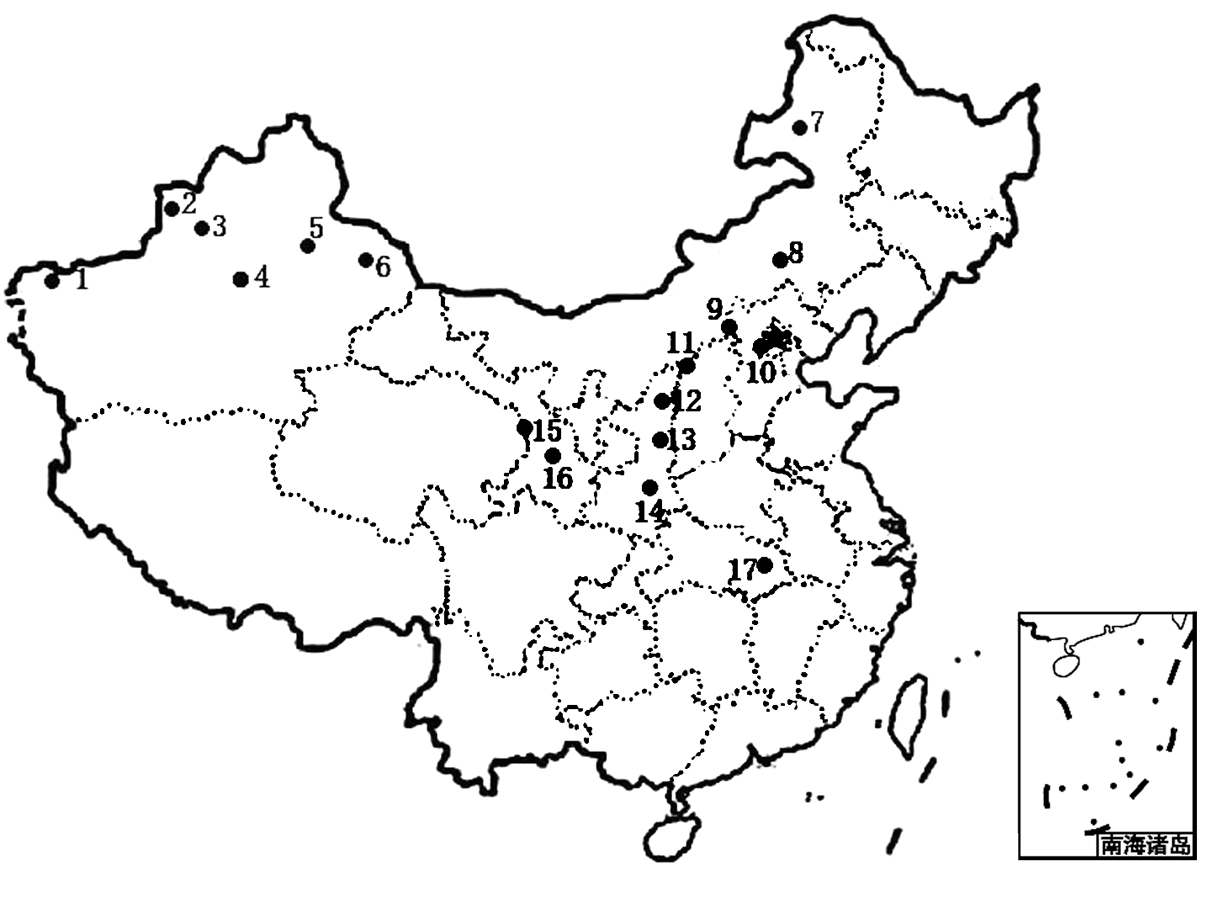
图1 天蓝苜蓿17个居群的具体采样点分布(居群代码同 表1)
Fig. 1 Map showing the distribution of the sampled 17 Medicago lupulina populations. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 居群 Population | 经纬度 Locality | 采样数目 Sample size |
|---|---|---|
| 新疆 Xinjiang | ||
| 1 喀什 Kashi | 39.44° N, 75.988° E | 23 |
| 2 伊犁 Yili | 43.88° N, 81.305° E | 20 |
| 3 那拉提 Nalati | 43.45° N, 83.283° E | 20 |
| 4 库尔勒 Korla | 41.75° N, 86.128° E | 17 |
| 5 奇台 Qitai | 43.70° N, 89.604° E | 23 |
| 6 巴里坤 Balikun | 43.58° N, 93.008° E | 20 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | ||
| 7 海拉尔 Hailar | 48.90° N, 119.837° E | 18 |
| 8 白音敖包 Baiyinaobao | 43.53° N, 117.236° E | 21 |
| 9 兴和 Xinghe | 40.89° N, 113.885° E | 21 |
| 北京 Beijing | ||
| 10 东灵山 Dongling Mountain | 39.96° N, 115.439° E | 12 |
| 山西 Shanxi | ||
| 11 偏关 Pianguan | 39.44° N, 111.461° E | 22 |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | ||
| 12 鱼河 Yuhe | 37.98° N, 109.853° E | 23 |
| 13 南泥湾 Nanniwan | 36.32° N, 109.651° E | 20 |
| 14 西安 Xi’an | 34.28° N, 108.958° E | 27 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | ||
| 15 朱岔 Zhucha | 36.94° N, 102.589° E | 21 |
| 16 兴隆山 Xinglong Mountain 湖北 Hubei | 35.78° N, 104.048° E | 20 |
| 17 武汉 Wuhan | 30.55° N, 114.415° E | 26 |
| 总计 Total | 354 |
表1 天蓝苜蓿的采样信息
Table 1 Sampling sites and sample size of Medicago lupulinapopulations
| 居群 Population | 经纬度 Locality | 采样数目 Sample size |
|---|---|---|
| 新疆 Xinjiang | ||
| 1 喀什 Kashi | 39.44° N, 75.988° E | 23 |
| 2 伊犁 Yili | 43.88° N, 81.305° E | 20 |
| 3 那拉提 Nalati | 43.45° N, 83.283° E | 20 |
| 4 库尔勒 Korla | 41.75° N, 86.128° E | 17 |
| 5 奇台 Qitai | 43.70° N, 89.604° E | 23 |
| 6 巴里坤 Balikun | 43.58° N, 93.008° E | 20 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | ||
| 7 海拉尔 Hailar | 48.90° N, 119.837° E | 18 |
| 8 白音敖包 Baiyinaobao | 43.53° N, 117.236° E | 21 |
| 9 兴和 Xinghe | 40.89° N, 113.885° E | 21 |
| 北京 Beijing | ||
| 10 东灵山 Dongling Mountain | 39.96° N, 115.439° E | 12 |
| 山西 Shanxi | ||
| 11 偏关 Pianguan | 39.44° N, 111.461° E | 22 |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | ||
| 12 鱼河 Yuhe | 37.98° N, 109.853° E | 23 |
| 13 南泥湾 Nanniwan | 36.32° N, 109.651° E | 20 |
| 14 西安 Xi’an | 34.28° N, 108.958° E | 27 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | ||
| 15 朱岔 Zhucha | 36.94° N, 102.589° E | 21 |
| 16 兴隆山 Xinglong Mountain 湖北 Hubei | 35.78° N, 104.048° E | 20 |
| 17 武汉 Wuhan | 30.55° N, 114.415° E | 26 |
| 总计 Total | 354 |
| 位点 Locus | 等位基因数 A | 预期杂合度 HE | 观察杂合度 HO | 遗传分化系数 FST | 基因流 Nm | 遗传分化系数RST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTIC189 | 10 | 0.256 | 0.017 | 0.555 | 0.201 | 0.478 |
| MTIC432 | 5 | 0.177 | 0.034 | 0.643 | 0.139 | 0.58 |
| MTIC339 | 4 | 0.039 | 0.000 | 0.058 | 4.038 | -0.004 |
| MTIC345 | 8 | 0.320 | 0.085 | 0.463 | 0.290 | 0.447 |
| MTIC210 | 10 | 0.267 | 0.005 | 0.564 | 0.193 | 0.636 |
| MTIC14 | 6 | 0.180 | 0.000 | 0.604 | 0.164 | 0.703 |
| MTIC188 | 11 | 0.247 | 0.014 | 0.612 | 0.159 | 0.619 |
| MAA660870 | 5 | 0.157 | 0.003 | 0.605 | 0.163 | 0.508 |
| MtSSRNFAL05 | 7 | 0.266 | 0.017 | 0.649 | 0.135 | 0.528 |
| 平均 Mean | 7.333 | 0.212 | 0.020 | 0.528 | 0.224 | 0.499 |
表2 天蓝苜蓿9个EST-SSR位点的遗传多样性
Table 2 Genetic diversity in Medicago lupulina at nine EST-SSR loci
| 位点 Locus | 等位基因数 A | 预期杂合度 HE | 观察杂合度 HO | 遗传分化系数 FST | 基因流 Nm | 遗传分化系数RST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTIC189 | 10 | 0.256 | 0.017 | 0.555 | 0.201 | 0.478 |
| MTIC432 | 5 | 0.177 | 0.034 | 0.643 | 0.139 | 0.58 |
| MTIC339 | 4 | 0.039 | 0.000 | 0.058 | 4.038 | -0.004 |
| MTIC345 | 8 | 0.320 | 0.085 | 0.463 | 0.290 | 0.447 |
| MTIC210 | 10 | 0.267 | 0.005 | 0.564 | 0.193 | 0.636 |
| MTIC14 | 6 | 0.180 | 0.000 | 0.604 | 0.164 | 0.703 |
| MTIC188 | 11 | 0.247 | 0.014 | 0.612 | 0.159 | 0.619 |
| MAA660870 | 5 | 0.157 | 0.003 | 0.605 | 0.163 | 0.508 |
| MtSSRNFAL05 | 7 | 0.266 | 0.017 | 0.649 | 0.135 | 0.528 |
| 平均 Mean | 7.333 | 0.212 | 0.020 | 0.528 | 0.224 | 0.499 |
| 居群 Population | 平均等位基因数na | 有效等位基因数ne | 观察杂合度 Ho | 预期杂合度 HE | 近交系数 F | 自交率 s | 多态率 PPL (%) | 私有基因数 Private alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 喀什 Kashi | 2.444 | 1.746 | 0.019 | 0.346 | 0.947 | 0.973 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 2 伊犁 Yili | 3.556 | 1.717 | 0.056 | 0.342 | 0.845 | 0.916 | 100 | 5 |
| 3 那拉提 Nalati | 2.667 | 1.868 | 0.028 | 0.388 | 0.932 | 0.965 | 88.9 | 1 |
| 4 库尔勒 Korla | 2.222 | 1.779 | 0.007 | 0.348 | 0.982 | 0.991 | 77.8 | 1 |
| 5 奇台 Qitai | 2.111 | 1.380 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 6 巴里坤 Balikun | 1.667 | 1.196 | 0.034 | 0.118 | 0.725 | 0.841 | 33.3 | 0 |
| 7 海拉尔 Hailar | 2.111 | 1.137 | 0.025 | 0.107 | 0.781 | 0.877 | 66.7 | 1 |
| 8 白音敖包 Baiyinaobao | 1.778 | 1.196 | 0.011 | 0.145 | 0.93 | 0.964 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 9 兴和 Xinghe | 1.889 | 1.223 | 0.011 | 0.153 | 0.931 | 0.964 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 10 东灵山 Dongling Mountain | 2.111 | 1.467 | 0.009 | 0.270 | 0.968 | 0.984 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 11 偏关 Pianguan | 2.000 | 1.183 | 0.035 | 0.137 | 0.752 | 0.858 | 88.9 | 0 |
| 12 鱼河 Yuhe | 2.333 | 1.294 | 0.034 | 0.188 | 0.824 | 0.904 | 66.7 | 1 |
| 13 南泥湾 Nanniwan | 1.667 | 1.246 | 0.000 | 0.152 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 55.6 | 1 |
| 14 西安 Xi’an | 1.444 | 1.049 | 0.012 | 0.042 | 0.716 | 0.835 | 33.3 | 0 |
| 15 朱岔 Zhucha | 3.556 | 1.448 | 0.042 | 0.252 | 0.840 | 0.913 | 77.8 | 8 |
| 16 兴隆山 Xinglongshan | 2.333 | 1.576 | 0.000 | 0.302 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 17 武汉 Wuhan | 2.333 | 1.122 | 0.009 | 0.104 | 0.921 | 0.959 | 100 | 3 |
| 平均 Mean | 2.248 | 1.390 | 0.020 | 0.212 | 0.888 | 0.938 | 71.9 | 1 |
表3 天蓝苜蓿17个自然居群的遗传多样性参数检测
Table 3 Genetic variability estimates for 17 Medicago lupulinapopulations
| 居群 Population | 平均等位基因数na | 有效等位基因数ne | 观察杂合度 Ho | 预期杂合度 HE | 近交系数 F | 自交率 s | 多态率 PPL (%) | 私有基因数 Private alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 喀什 Kashi | 2.444 | 1.746 | 0.019 | 0.346 | 0.947 | 0.973 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 2 伊犁 Yili | 3.556 | 1.717 | 0.056 | 0.342 | 0.845 | 0.916 | 100 | 5 |
| 3 那拉提 Nalati | 2.667 | 1.868 | 0.028 | 0.388 | 0.932 | 0.965 | 88.9 | 1 |
| 4 库尔勒 Korla | 2.222 | 1.779 | 0.007 | 0.348 | 0.982 | 0.991 | 77.8 | 1 |
| 5 奇台 Qitai | 2.111 | 1.380 | 0.000 | 0.214 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 6 巴里坤 Balikun | 1.667 | 1.196 | 0.034 | 0.118 | 0.725 | 0.841 | 33.3 | 0 |
| 7 海拉尔 Hailar | 2.111 | 1.137 | 0.025 | 0.107 | 0.781 | 0.877 | 66.7 | 1 |
| 8 白音敖包 Baiyinaobao | 1.778 | 1.196 | 0.011 | 0.145 | 0.93 | 0.964 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 9 兴和 Xinghe | 1.889 | 1.223 | 0.011 | 0.153 | 0.931 | 0.964 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 10 东灵山 Dongling Mountain | 2.111 | 1.467 | 0.009 | 0.270 | 0.968 | 0.984 | 77.8 | 0 |
| 11 偏关 Pianguan | 2.000 | 1.183 | 0.035 | 0.137 | 0.752 | 0.858 | 88.9 | 0 |
| 12 鱼河 Yuhe | 2.333 | 1.294 | 0.034 | 0.188 | 0.824 | 0.904 | 66.7 | 1 |
| 13 南泥湾 Nanniwan | 1.667 | 1.246 | 0.000 | 0.152 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 55.6 | 1 |
| 14 西安 Xi’an | 1.444 | 1.049 | 0.012 | 0.042 | 0.716 | 0.835 | 33.3 | 0 |
| 15 朱岔 Zhucha | 3.556 | 1.448 | 0.042 | 0.252 | 0.840 | 0.913 | 77.8 | 8 |
| 16 兴隆山 Xinglongshan | 2.333 | 1.576 | 0.000 | 0.302 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 17 武汉 Wuhan | 2.333 | 1.122 | 0.009 | 0.104 | 0.921 | 0.959 | 100 | 3 |
| 平均 Mean | 2.248 | 1.390 | 0.020 | 0.212 | 0.888 | 0.938 | 71.9 | 1 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d. f. | 离差平方和(SSD) Sum of squares | 方差分量 Variance components | 方差分量比例(%) Percentage of variation | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间 Among populations | 16 | 951.886 | Va = 1.38653 | 59.02 | P<0.001 |
| 居群内个体间 Within populations | 337 | 619.494 | Vb = 0.87535 | 37.26 | P<0.001 |
| 个体内 Within individuals | 354 | 31.000 | Vc = 0.08757 | 3.73 | P<0.001 |
| 总计 Total | 707 | 1602.380 | 2.34945 |
表4 居群遗传结构的分子方差分析
Table 4 Molecular variance (AMOVA) analysis based on EST-SSR markers for Medicago lupulina
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d. f. | 离差平方和(SSD) Sum of squares | 方差分量 Variance components | 方差分量比例(%) Percentage of variation | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间 Among populations | 16 | 951.886 | Va = 1.38653 | 59.02 | P<0.001 |
| 居群内个体间 Within populations | 337 | 619.494 | Vb = 0.87535 | 37.26 | P<0.001 |
| 个体内 Within individuals | 354 | 31.000 | Vc = 0.08757 | 3.73 | P<0.001 |
| 总计 Total | 707 | 1602.380 | 2.34945 |
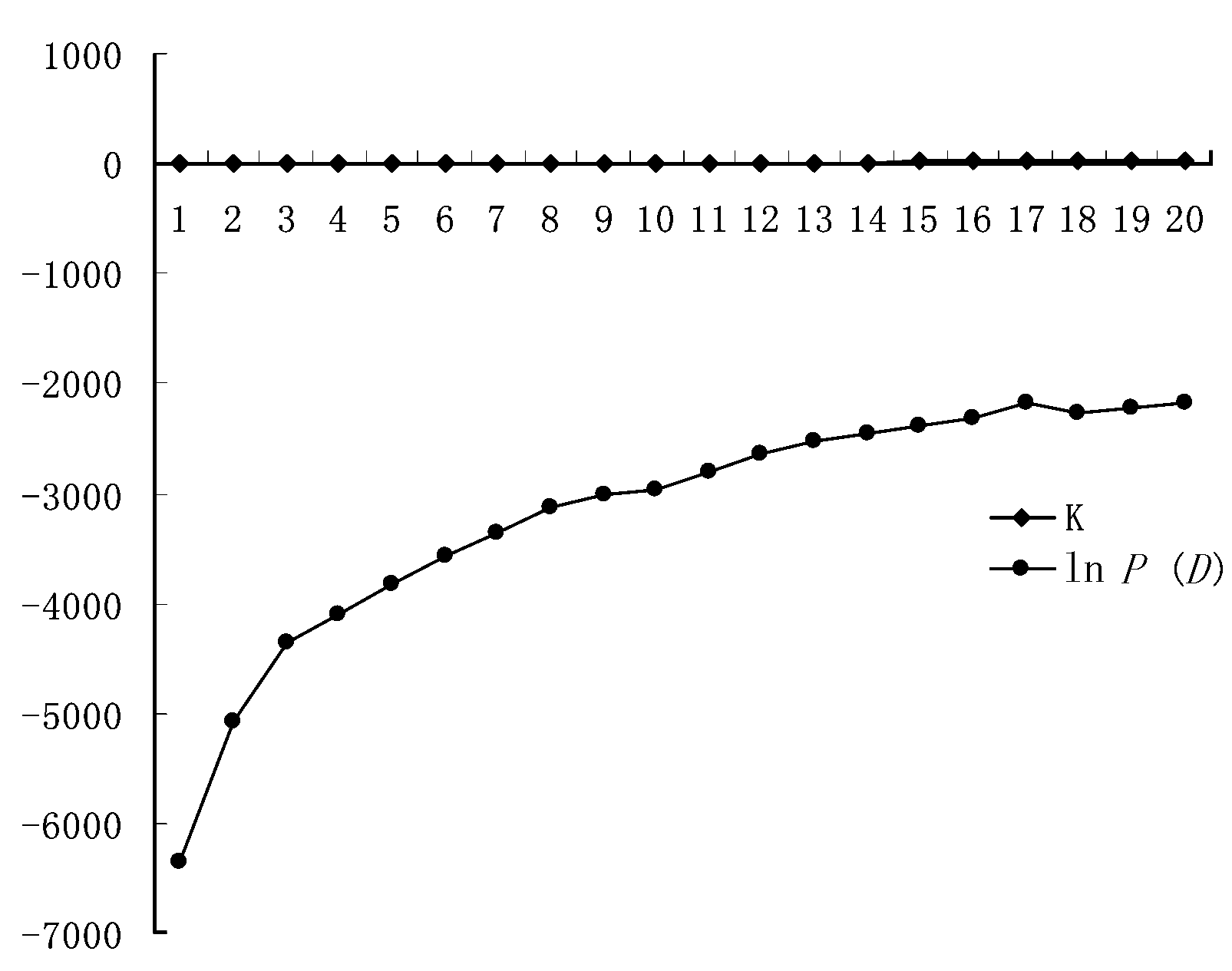
图2 STRUCTURE分析得到的居群分组概率的对数值(K=1-20)
Fig. 2 Estimated posterior probability of K (1-20) for Medicago lupulina, where K represents the number of clusters.
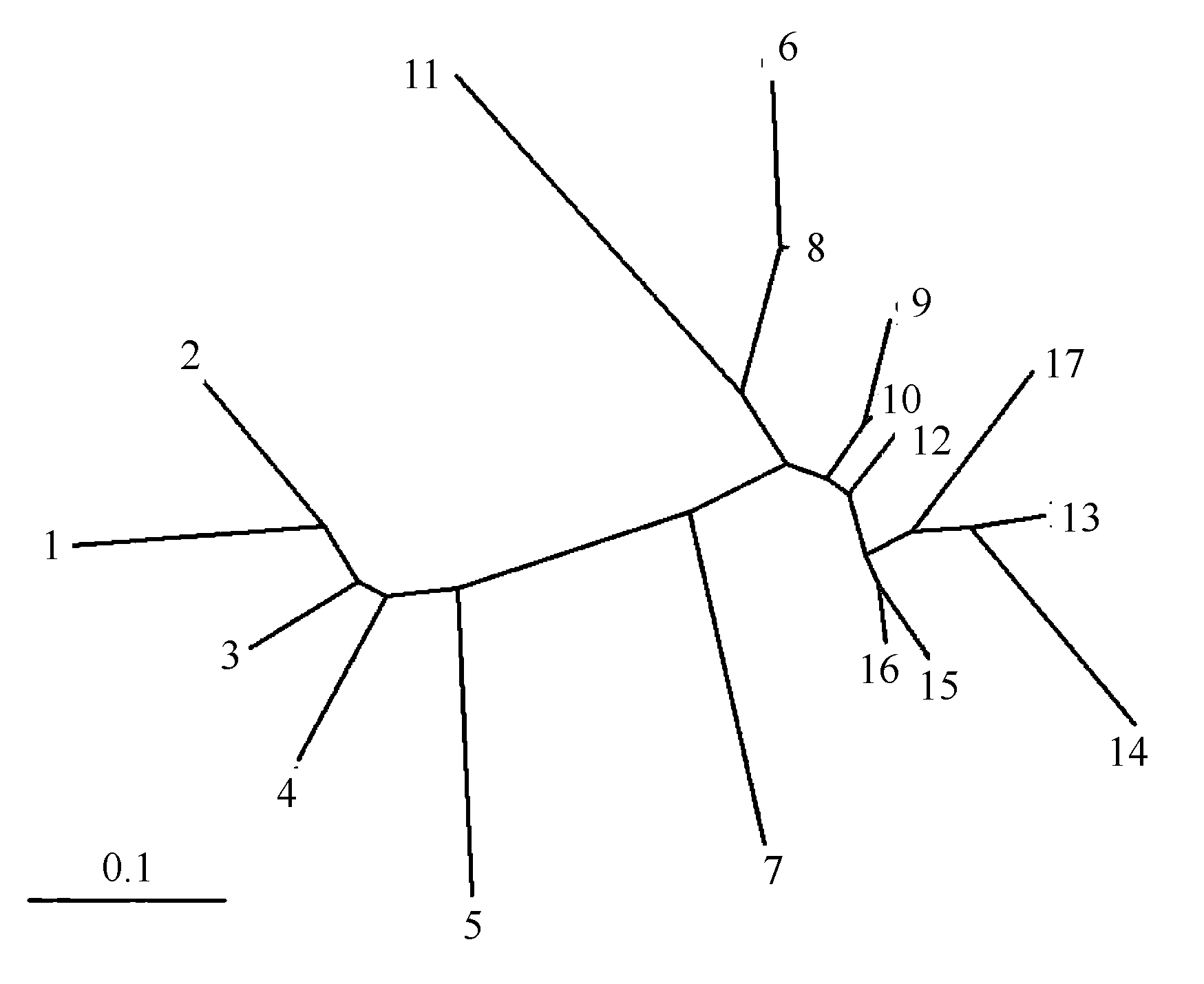
图4 天蓝苜蓿17个居群的聚类分析图 (居群编码见表1)
Fig. 4 Unrooted neighbour-joining tree showing relationships between the 17 Medicago lupulina populations. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | Bohonak AJ (2002) IBD (Isolation by Distance): a program for analyses of isolation by distance. Journal of Heredity, 93,153-154. |
| [2] | Bonnin I, Ronfort J, Wozniak F, Olivier I (2001) Spatial effects and rare outcrossing events in Medicago truncatula (Fabaceae) . Molecular Ecology, 10,1371-1383. |
| [3] | Bouck A, Vision T (2007) The molecular ecologist’s guide to expressed sequence tags. Molecular Ecology, 16,907-924. |
| [4] | Cao ZZ (曹致中), Feng YQ (冯毓琴), Ma HL (马晖玲), Liu XN (柳小妮), Zhou YL (周玉雷), Xu ZM (徐智明) (2003) Medicago lupulina—beautiful water-saving and easily-maintained turf legume . Pratacultural Science (草业科学), 20(4),58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chabane K, Ablett GA, Cordeiro GM, Valkoun J, Henry RJ (2005) EST versus genomic derived microsatellite markers for genotyping wild and cultivated barley. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 52,903-909. |
| [6] | Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S, Chen X, Lipovich L, McCouch SR, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S (2000) Diversity of microsatellites derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice ( Oryza sativa L.) . Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 100,713-722. |
| [7] | Clapham AR, Tutin TG, Warburg EF (1962) Flora of the British Isles. Cambridge University Press,Cambridge, UK. |
| [8] | Clauss MJ, Mitchell-Olds T (2006) Population genetic structure of Arabidopsis lyrata in Europe . Molecular Ecology, 15,2753-2766. |
| [9] | Crow JK, Kimura M (1970) An Introduction to Population Genetic Theory. Harper and Row, New York. |
| [10] | Diwan N, Bouton JH, Kochert G, Cregan PB (2000) Mapping of simple sequence repeat (SSR) DNA markers in diploid and tetraploid alfalfa. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 101,165-172. |
| [11] | Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19,11-15. |
| [12] | Ellis JR, Burke JM (2007) EST-SSRs as a resource for population genetic analyses. Heredity, 99,125-132. |
| [13] | Ennos RA (1994) Estimating the relative rates of pollen and seed migration among plant populations. Heredity, 72,250-259. |
| [14] | Eujayl I, Sledge MK, Wang L, May GD, Chekhovskiy K, Zwonitzer J, Mian MAR (2004) Medicago truncatula EST-SSRs reveal cross-species genetic markers for Medicago spp. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 108,414-422. |
| [15] | Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Molecular Ecology, 14,2611-2620. |
| [16] | Flajoulot S, Ronfort J, Baudouin P, Barre P, Huguet T, Huyghe C, Julier B (2005) Genetic diversity among alfalfa ( Medicago sativa) cultivars coming from a breeding program, using SSR markers . Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 111,1420-1429. |
| [17] | Fowler DP (1965) Effects of inbreeding in red pine, Pinus resinosa Ait. Ⅱ. Pollination studies . Silvae Genetica, 14,12-23. |
| [18] | Goudet J (2001) FSTAT, A Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices, version 2. 9.3. http://www.unil.ch/izea/softwares/fstat.html. |
| [19] | Govindaraju DR (1988) Relationship between dispersal ability and levels of gene flow in plants. Oikos, 52,31-35. |
| [20] |
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Sharma S, Singh R, Kumar N, Balyan HS (2003) Transferable EST-SSR markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity in bread wheat. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 270,315-323.
URL PMID |
| [21] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1996) Effects of life-history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 351,1291-1298. |
| [22] | Julier B, Flajoulot S, Barre P, Cardinet G, Santoni S, Huguet T, Huyghe C (2003) Construction of two genetic linkage maps in cultivated tetraploid alfalfa ( Medicago sativa) using microsatellite and AFLP markers . BMC Plant Biology, 3,9. |
| [23] |
Kuroda Y, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Vaughan A (2006) Population genetic structure of Japanese wild soybean ( Glycine soja) based on microsatellite variation . Molecular Ecology, 15,959-974.
URL PMID |
| [24] | Lammerink J (1968) Genetic variability in commencement of flowering in Medicago lupulina L. in the south island of New Zealand . New Zealand Journal of Botany, 6,33-42. |
| [25] | Langella O (2000) Populations 1.2: Population Genetic Software (Individuals or Population Distance, Phylogenetic Trees). http://bioinformatics.org/~tryphon/popula- tions/. |
| [26] | Loveless MD, Hamrick JL (1984) Ecological determinants of genetic structure in plant populations. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 15,65-95. |
| [27] |
Mable BK, Adam A (2007) Patterns of genetic diversity in outcrossing and selfing populations of Arabidopsis lyrata. Molecular Ecology, 16,3565-3580.
URL PMID |
| [28] | Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Research, 27,209-220. |
| [29] |
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 19,153-170.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Moyle LC (2006) Correlates of genetic differentiation and isolation by distance in 17 congeneric Silene species . Molecular Ecology, 15,1067-1081. |
| [31] |
Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Molecular Ecology, 13,1143-1155.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Pashley CH, Ellis JR, McCauley DE, Burke JM (2006) EST databases as a source for molecular markers: lessons from Helianthus. Journal of Heredity, 97,381-388.
URL PMID |
| [33] | Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 12,357-358. |
| [34] | Pavone LV, Reader RJ (1985) Effect of microtopography on the survival and reproduction of Medicago lupulina . The Journal of Ecology, 73,685-694. |
| [35] | Peakall R, Gilmore S, Keys W, Morgante M, Rafalski A (1998) Cross species amplification of soybean ( Glycine max) simple sequence repeat (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: implication for transferability of SSRs in plants . Molecular Biology and Evolution, 15,1275-1287. |
| [36] | Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenALEx6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Molecular Ecology Notes, 6,288-295. |
| [37] | Pritchard JK, Stephans M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics, 155,945-959. |
| [38] | Pritchard JK, Wen XQ, Fslush D (2007) STRUCTURE: Documentation for Structure Software: version 2.2. http://pritch.bsd.uchicago.edu/software. |
| [39] | Rice WR (1989) Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution, 43,223-225. |
| [40] | Rousset F (1997) Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance . Genetics, 145,1219-1228. |
| [41] | Sanguinetti CJ, Dias NE, Simpson G (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyaerylamide gels. Biotechniques, 17,915-919. |
| [42] | Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) ARLEQUIN ver. 2.000: A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis. Genetics and Biochemistry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Switzerland. |
| [43] | Sidhu SS (1971) Some Aspects of the Ecology of Black Medick (Medicago lupulina L.). PhD dissertation, University of Western Ontario., . |
| [44] | Slatkin M, Barton NH (1989) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution, 43,1349-1368. |
| [45] | StenØien HK, Fenster CB, Tonteri A, Savolainen O (2005) Genetic variability in natural populations of Arabidopsis thaliana in northern Europe . Molecular Ecology, 14,137-148. |
| [46] | Turkington RA, Cavers PB (1979) The biology of Canadian weeds. 33. Medicago lupulina L. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 59,99-110. |
| [47] | Wei Z (韦直), Huang YZ (黄以之) (1998) Leguminosae. In:Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (中国植物志), Tomus 42, pp.314-316. Science Press, Beijing.. (in Chinese) |
| [48] | Wright S (1965) The interpretations of population structure by F-statistics with special regards to systems of mating . Evolution, 19,395-420. |
| [49] | Zhu BC (朱邦长), He SJ (何胜江), Zhang CQ (张川黔), Song GX (宋高翔) (1996) Guizhou natural legume herbage—introduction and domestication of black medick (Medicago lupulina L.). Guizhou Agricultural Sciences (贵州农业科学), 24(4),36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [4] | 景昭阳, 程可光, 舒恒, 马永鹏, 刘平丽. 全基因组重测序方法在濒危植物保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [8] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [11] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [12] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [13] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [14] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [15] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn