



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (3): 271-278. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07312
收稿日期:2007-10-17
接受日期:2008-01-21
出版日期:2008-05-20
发布日期:2008-05-20
通讯作者:
李巧明
作者简介:*E-mail:lqm@xtbg.ac.cn基金资助:Received:2007-10-17
Accepted:2008-01-21
Online:2008-05-20
Published:2008-05-20
Contact:
Qiaoming Li
摘要:
羽叶金合欢(Acacia pennata)是一种重要的经济植物。本研究使用微卫星(SSR)分子标记技术对分布于云南西双版纳地区的7个羽叶金合欢自然居群进行了遗传多样性和居群遗传结构的研究, 旨在从分子水平探讨其自然居群的遗传多样性, 制定科学的保护策略, 为今后的持续利用提供科学依据。我们用筛选出的6对SSR引物对采自7个自然居群的124个个体进行了扩增, 共检测到23个等位基因。平均观察等位基因数(Na)为3.381, 有效等位基因数(Ne)为2.460, 平均期望杂合度(He)为0.573, Nei’s多样性指数(h)为0.567。其中景洪居群具有较高的遗传多样性, 曼腊居群遗传多样性相对较低。遗传分化系数FST仅为0.113。结果表明羽叶金合欢的自然居群具有较高的遗传多样性水平, 居群间分化较小, 遗传变异主要来源于居群内。羽叶金合欢为多年生植物, 分布范围广泛, 这可能是其具有较高水平遗传多样性的原因; 同时其繁育系统可能为异交, 种子可远距离传播, 这些特性也可能导致其较高的遗传多样性水平和较低的居群遗传分化。我们建议在对羽叶金合欢进行迁地保护时, 要在遗传多样性较高的居群内进行大量取样, 同时也要对不同居群进行取样。
高洁, 李巧明 (2008) 云南西双版纳地区羽叶金合欢的遗传多样性研究. 生物多样性, 16, 271-278. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07312.
Jie Gao, Qiaoming Li (2008) Genetic diversity of natural populations of Acacia pennatain Xishuangbanna, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 16, 271-278. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07312.
| 居群代号 Population code | 采样地 Origin | 经纬度 Location | 样本量 Sample size | 生境 Habitat | 伴生种 Companion species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大渡岗DDG | 景洪市大渡岗 Dadugang, Jinghong City | 100.91° E 22.50° N | 17 | 山脚、沟谷 Mountain foot, ravine forest | 绒毛番龙眼 Pometia tomentosa 千果榄仁 Terminalia myriocarpa |
| 大勐龙DML | 勐海县大勐龙 Damenglong, Menghai County | 100.50° E 21.50° N | 20 | 沟谷林 Ravine forest | 番龙眼 P. pinnata 油朴 Celtis wighetii 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var.pseudoverticillata |
| 普文 PW | 景洪市普文 Puwen, Jinghong City | 101.38° E 22.55° N | 15 | 沟谷林 Ravine forest | 毛麻楝 Chukrasia tabularis var. velutina, 油朴Celtis wighetii |
| 景洪 JH | 景洪市勐罕 Menghan, Jinghong City | 100.78° E 21.93° N | 18 | 沟谷林、低山 Ravine forest, hill | 番龙眼 P. pinnata 油朴 Celtis wighetii 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var.pseudoverticillata |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 勐腊县勐仑 Menglun, Mengla County | 101.25° E 21.91° N | 20 | 石灰山、山脚Limestone forest, mountain foot | 尖叶闭花木 Cleistanthus sumatranus 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var. pseudoverticillata |
| 勐腊 BB | 勐腊县补蚌 Bubeng, Mengla County | 101.63° E 21.53° N | 17 | 河边、沟谷林 River bank, ravine forest | 云南厚壳桂 Cryptocarya yunnanensis 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis |
| 曼腊 ML | 勐腊县曼腊 Manla, Mengla County | 101.50° E 22.21° N | 17 | 低中山坡、沟谷林Mountain slope, ravine forest | 长果木棉 Bombax insigne 一担柴 Colona floribunda 翅果刺桐 Erythrina subumbrans |
| 总计 Total | 124 |
表1 羽叶金合欢自然居群的采样数目及位置
Table 1 Locations and sample size of natural populations of Acacia pennata
| 居群代号 Population code | 采样地 Origin | 经纬度 Location | 样本量 Sample size | 生境 Habitat | 伴生种 Companion species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大渡岗DDG | 景洪市大渡岗 Dadugang, Jinghong City | 100.91° E 22.50° N | 17 | 山脚、沟谷 Mountain foot, ravine forest | 绒毛番龙眼 Pometia tomentosa 千果榄仁 Terminalia myriocarpa |
| 大勐龙DML | 勐海县大勐龙 Damenglong, Menghai County | 100.50° E 21.50° N | 20 | 沟谷林 Ravine forest | 番龙眼 P. pinnata 油朴 Celtis wighetii 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var.pseudoverticillata |
| 普文 PW | 景洪市普文 Puwen, Jinghong City | 101.38° E 22.55° N | 15 | 沟谷林 Ravine forest | 毛麻楝 Chukrasia tabularis var. velutina, 油朴Celtis wighetii |
| 景洪 JH | 景洪市勐罕 Menghan, Jinghong City | 100.78° E 21.93° N | 18 | 沟谷林、低山 Ravine forest, hill | 番龙眼 P. pinnata 油朴 Celtis wighetii 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var.pseudoverticillata |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 勐腊县勐仑 Menglun, Mengla County | 101.25° E 21.91° N | 20 | 石灰山、山脚Limestone forest, mountain foot | 尖叶闭花木 Cleistanthus sumatranus 轮叶戟 Lasiococca comberi var. pseudoverticillata |
| 勐腊 BB | 勐腊县补蚌 Bubeng, Mengla County | 101.63° E 21.53° N | 17 | 河边、沟谷林 River bank, ravine forest | 云南厚壳桂 Cryptocarya yunnanensis 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis |
| 曼腊 ML | 勐腊县曼腊 Manla, Mengla County | 101.50° E 22.21° N | 17 | 低中山坡、沟谷林Mountain slope, ravine forest | 长果木棉 Bombax insigne 一担柴 Colona floribunda 翅果刺桐 Erythrina subumbrans |
| 总计 Total | 124 |
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 原始编号 Original code | 引物来源 Source | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4 | GTCGCGTACACAGACACAGT GGCGCACCTCTCTCTCTCT | 50 | Am367 | Acacia mangium | Butcher et al.( |
| P5 | GGCGCAACTCTCTCTCTCT TTGGTCACTTAGCGCATGCC | 48 | Am429 | A. mangium | Butcher et al.( |
| P9 | GAGGTAATATTTTGAATTCCTTGAAC GGTGTATACCTCTTTCCTGTGG | 48 | AH08 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
| P11 | CGCAACTCCATCTGATTTACTG TTATGTTGGGTTAATACGCTAACTG | 46 | AH18 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
| P13 | GTGAAGGCTCTCTCTCTCT GGAGATGGATAGAGATGGCC | 48 | Ab22 | A. brevispica | Otero-Arnaiz et al.( |
| P18 | GTCGCGTACACAGACACAGT GGCGCACCTCTCTCTCTCT | 50 | AH37 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
表2 筛选出的用于羽叶金合欢扩增的SSR引物序列及退火温度
Table 2 Primer sequences, annealing temperature of PCR amplification for Acacia pennata
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 原始编号 Original code | 引物来源 Source | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4 | GTCGCGTACACAGACACAGT GGCGCACCTCTCTCTCTCT | 50 | Am367 | Acacia mangium | Butcher et al.( |
| P5 | GGCGCAACTCTCTCTCTCT TTGGTCACTTAGCGCATGCC | 48 | Am429 | A. mangium | Butcher et al.( |
| P9 | GAGGTAATATTTTGAATTCCTTGAAC GGTGTATACCTCTTTCCTGTGG | 48 | AH08 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
| P11 | CGCAACTCCATCTGATTTACTG TTATGTTGGGTTAATACGCTAACTG | 46 | AH18 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
| P13 | GTGAAGGCTCTCTCTCTCT GGAGATGGATAGAGATGGCC | 48 | Ab22 | A. brevispica | Otero-Arnaiz et al.( |
| P18 | GTCGCGTACACAGACACAGT GGCGCACCTCTCTCTCTCT | 50 | AH37 | A. mangium A. auriculiformis | Ng et al.( |
| 基因座 Locus | 样本量 Sample size | 观察等位 基因数Na | 有效等位 基因数Ne | Nei’s基因 多样性h | 观察杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 近交系数 FIS | 基因分化系数FST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4 | 124 | 5.286 | 3.113 | 0.787 | 0.431 | 0.643 | 0.331 | 0.182 |
| P5 | 124 | 3.714 | 2.705 | 0.739 | 0.460 | 0.610 | 0.246 | 0.175 |
| P9 | 124 | 3.000 | 2.478 | 0.643 | 0.518 | 0.592 | 0.125 | 0.079 |
| P11 | 124 | 2.000 | 1.877 | 0.485 | 0.449 | 0.466 | 0.036 | 0.039 |
| P13 | 124 | 3.286 | 2.251 | 0.578 | 0.528 | 0.602 | -0.140 | 0.086 |
| P18 | 124 | 3.000 | 2.336 | 0.632 | 0.509 | 0.560 | 0.091 | 0.114 |
| 平均 Mean | 124 | 3.381 | 2.460 | 0.644 | 0.483 | 0.573 | 0.115 | 0.113 |
表3 羽叶金合欢物种水平的遗传多样度与遗传分化
Table 3 Genetic diversity and genetic differentiation ofAcacia pennata at species level
| 基因座 Locus | 样本量 Sample size | 观察等位 基因数Na | 有效等位 基因数Ne | Nei’s基因 多样性h | 观察杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 近交系数 FIS | 基因分化系数FST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4 | 124 | 5.286 | 3.113 | 0.787 | 0.431 | 0.643 | 0.331 | 0.182 |
| P5 | 124 | 3.714 | 2.705 | 0.739 | 0.460 | 0.610 | 0.246 | 0.175 |
| P9 | 124 | 3.000 | 2.478 | 0.643 | 0.518 | 0.592 | 0.125 | 0.079 |
| P11 | 124 | 2.000 | 1.877 | 0.485 | 0.449 | 0.466 | 0.036 | 0.039 |
| P13 | 124 | 3.286 | 2.251 | 0.578 | 0.528 | 0.602 | -0.140 | 0.086 |
| P18 | 124 | 3.000 | 2.336 | 0.632 | 0.509 | 0.560 | 0.091 | 0.114 |
| 平均 Mean | 124 | 3.381 | 2.460 | 0.644 | 0.483 | 0.573 | 0.115 | 0.113 |
| 居群代号Population code | 样本量 Sample size | 观察等位 基因数 Na | 有效等位 基因数 Ne | Nei’s基因 多样性 h | 观察杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 近交系数 FIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大勐龙 DML | 20 | 3.500 | 2.779 | 0.607 | 0.480 | 0.607 | 0.200 |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 20 | 3.670 | 2.675 | 0.602 | 0.508 | 0.602 | 0.153 |
| 景洪 JH | 18 | 3.333 | 2.809 | 0.628 | 0.435 | 0.805 | 0.294 |
| 勐腊 BB | 17 | 3.500 | 2.490 | 0.582 | 0.510 | 0.582 | 0.111 |
| 大渡岗 DDG | 17 | 3.000 | 2.341 | 0.553 | 0.520 | 0.553 | 0.056 |
| 曼腊 ML | 17 | 3.167 | 1.920 | 0.464 | 0.529 | 0.464 | -0.150 |
| 普文 PW | 15 | 3.500 | 2.207 | 0.530 | 0.478 | 0.531 | 0.108 |
| 平均 Mean | 17.7 | 3.381 | 2.460 | 0.567 | 0.494 | 0.592 | 0.129 |
表4 羽叶金合欢居群水平的遗传多样度与遗传分化
Table 4 Genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Acacia pennatapopulations at population level
| 居群代号Population code | 样本量 Sample size | 观察等位 基因数 Na | 有效等位 基因数 Ne | Nei’s基因 多样性 h | 观察杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 近交系数 FIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大勐龙 DML | 20 | 3.500 | 2.779 | 0.607 | 0.480 | 0.607 | 0.200 |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 20 | 3.670 | 2.675 | 0.602 | 0.508 | 0.602 | 0.153 |
| 景洪 JH | 18 | 3.333 | 2.809 | 0.628 | 0.435 | 0.805 | 0.294 |
| 勐腊 BB | 17 | 3.500 | 2.490 | 0.582 | 0.510 | 0.582 | 0.111 |
| 大渡岗 DDG | 17 | 3.000 | 2.341 | 0.553 | 0.520 | 0.553 | 0.056 |
| 曼腊 ML | 17 | 3.167 | 1.920 | 0.464 | 0.529 | 0.464 | -0.150 |
| 普文 PW | 15 | 3.500 | 2.207 | 0.530 | 0.478 | 0.531 | 0.108 |
| 平均 Mean | 17.7 | 3.381 | 2.460 | 0.567 | 0.494 | 0.592 | 0.129 |
| 大勐龙 DML | 勐仑 MDJ | 景洪 JH | 勐腊 BB | 大渡岗 DDG | 曼腊 ML | 普文 PW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大勐龙 DML | **** | 0.861 | 0.868 | 0.877 | 0.872 | 0.850 | 0.785 |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 0.150 | **** | 0.873 | 0.839 | 0.805 | 0.736 | 0.799 |
| 景洪 JH | 0.141 | 0.135 | **** | 0.853 | 0.891 | 0.750 | 0.805 |
| 勐腊 BB | 0.131 | 0.175 | 0.159 | **** | 0.742 | 0.838 | 0.654 |
| 大渡岗 DDG | 0.137 | 0.217 | 0.115 | 0.299 | **** | 0.654 | 0.857 |
| 曼腊 ML | 0.163 | 0.307 | 0.288 | 0.177 | 0.425 | **** | 0.581 |
| 普文 PW | 0.242 | 0.224 | 0.216 | 0.424 | 0.154 | 0.542 | **** |
表5 羽叶金合欢7个居群间Nei’s遗传一致度(I)(对角线上方)和遗传距离(D)(对角线下方)
Table 5 Nei’s genetic identity (above diagonal) and genetic distance (below diagonal) among Acacia pennata populations
| 大勐龙 DML | 勐仑 MDJ | 景洪 JH | 勐腊 BB | 大渡岗 DDG | 曼腊 ML | 普文 PW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大勐龙 DML | **** | 0.861 | 0.868 | 0.877 | 0.872 | 0.850 | 0.785 |
| 勐仑 MDJ | 0.150 | **** | 0.873 | 0.839 | 0.805 | 0.736 | 0.799 |
| 景洪 JH | 0.141 | 0.135 | **** | 0.853 | 0.891 | 0.750 | 0.805 |
| 勐腊 BB | 0.131 | 0.175 | 0.159 | **** | 0.742 | 0.838 | 0.654 |
| 大渡岗 DDG | 0.137 | 0.217 | 0.115 | 0.299 | **** | 0.654 | 0.857 |
| 曼腊 ML | 0.163 | 0.307 | 0.288 | 0.177 | 0.425 | **** | 0.581 |
| 普文 PW | 0.242 | 0.224 | 0.216 | 0.424 | 0.154 | 0.542 | **** |
| 变异来源 Source of variance | 方差总和 SSD | 平均方差 MSD | 变异组分 Variance component | 变异百分率 Variation (%) | P* | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间 Among populations | 90.6407 | 15.107 | 0.6351 | 14.09 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 居群内 Within populations | 453.0690 | 3.872 | 3.8724 | 85.91 | <0.001 | |||||||
表6 羽叶金合欢居群的AMOVA分析
Table 6 AMOVA analysis of Acacia pennata populations
| 变异来源 Source of variance | 方差总和 SSD | 平均方差 MSD | 变异组分 Variance component | 变异百分率 Variation (%) | P* | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间 Among populations | 90.6407 | 15.107 | 0.6351 | 14.09 | <0.001 | |||||||
| 居群内 Within populations | 453.0690 | 3.872 | 3.8724 | 85.91 | <0.001 | |||||||
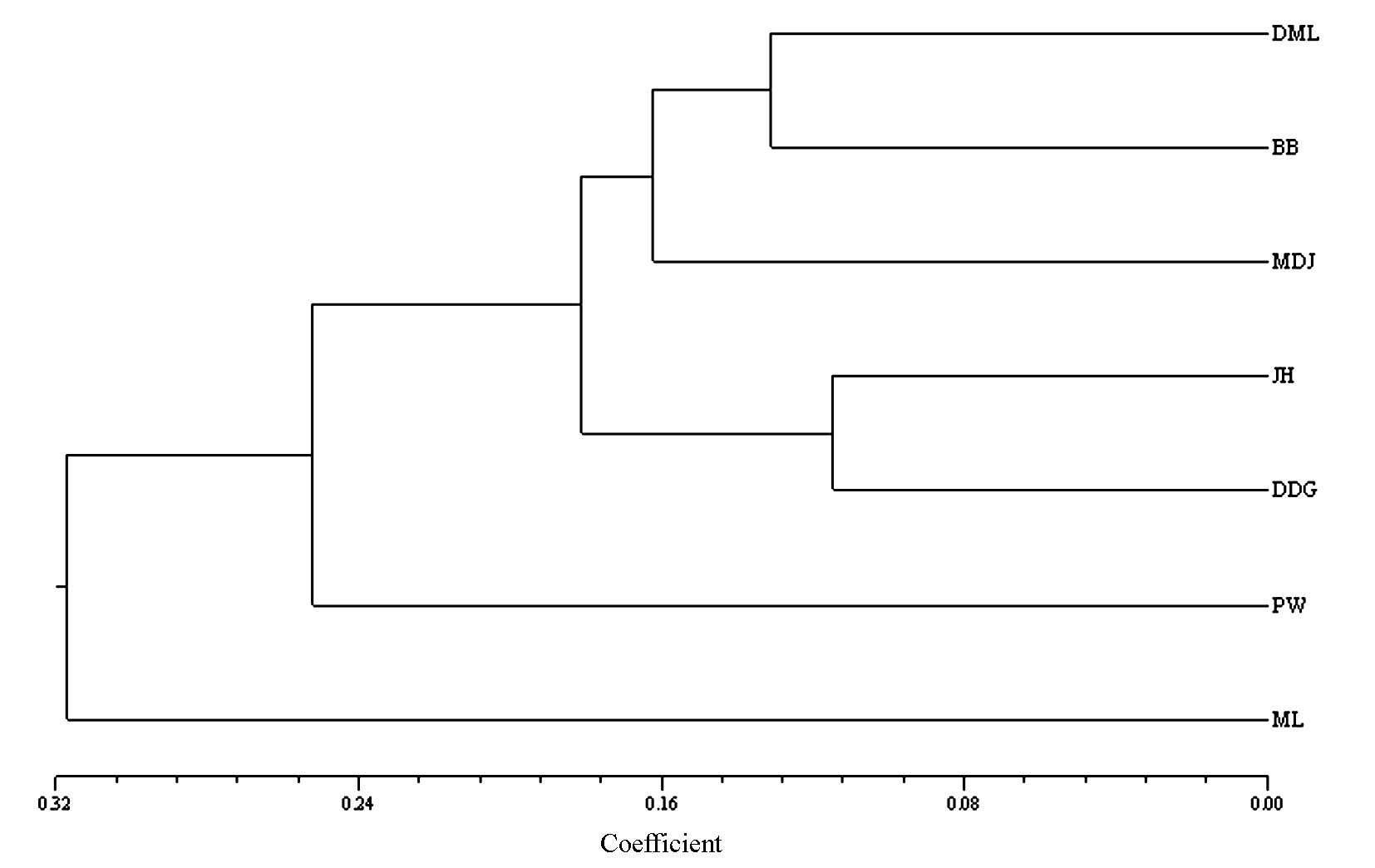
图1 基于Nei’s遗传距离绘制的羽叶金合欢居群的UPGMA聚类图(居群代号见表1)
Fig. 1 UPGMA dendrogram of Acacia pennatapopulations based on Nei’s genetic distance. Population codes correspond to those in Table 1.
| [1] | Bernhardt P, Kenrick J, Knox RB (1984) Pollination biology and the breeding system of Acacia retinodes (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae) . Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 71,17-29. |
| [2] | Broadhurst LM, Coates DJ (2002) Genetic diversity within and divergence between rare and geographically widespread taxa of the Acacia acuminata (Mimosaceae) complex . Heredity, 88,250-257. |
| [3] | Butcher PA, Decroocq S, Gray Y, Moran GF (2000) Development, inheritance and cross-species amplification of microsatellite markers from Acacia mangium. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 101,1282-1290. |
| [4] | Duan YP (段运平), Chen WG (陈卫国), Li MS (李明顺), Li XH (李新海), Liu X (刘雪), Tian QZ (田清震), Bai L (白丽), Zhang SH (张世煌) (2006) The genetic diversity among 27 maize populations based on SSR data. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 39,1102-1113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Excoffier L (1993) Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) Version 1.55. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Switzerland. |
| [6] | Gao J (高洁), Li QM (李巧明) (2008) The DNA extracting and SSR primer screening of Acacia pennata (Leguminosae). Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 30,64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Graham NS, Nigel ER, Matthew P, Pat GW (2003) Pollination ecology of Acacias (Fabaceae, Mimosoideae) . Australian Journal of Botany, 16,103-118. |
| [8] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1990) Allozyme diversity in plant species. In: Plant Population Genetics, Breeding and Genetics Resourses (eds Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL, Weir BS), pp.43-63. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA. |
| [9] | Hollingsworth PM, Dawson IK, Goodall CWP, Richardson JE, Weber JC, Montes CS, Pennington RT (2005) Do farmers reduce genetic diversity when they domesticate tropical trees? A case study from Amazonia. Molecular Ecology, 14,497-501. |
| [10] | Jiang ZL (姜志磊), Yang XM (杨欣明), Wang R (王瑞), Gao AN (高爱农), Li LH (李立会) (2005) Genetic diversity of Roegneria thoroldiana (Oliv.) Keng populations based on SSR analyses . Journal of Plant Genetic Resources (植物遗传资源学报), 6,315-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Kenrick J, Knox RB (1989) Quantitative analysis of self incompatibility in trees of seven species of Acacia. Heredity, 80,240-245. |
| [12] | Korron JD (1987) A comparison of levels of genetic polymorphism and self-compatibility in geographically restricted and widespread plant congeners. Ecology, 1,47-58. |
| [13] | Levinson G, Gutman GA (1987) Slipped strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4,203-281. |
| [14] |
Li CC, Horvitz DG (1953) Some methods of estimating the inbreeding coefficient. American Journal of Human Genetics, 5,107-117.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Madan KS, Golan GA, David D (2002) Population genetic structure and the conservation of isolated populations of Acacia raddiana in the Negev Desert . Biological Conservation, 108,119-127. |
| [16] | Miller MP (1997) Tools for Population Genetics Analysis (TFPGA), Version 1. 3. Department of Biological Sciences, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff. |
| [17] | Moore SS, Sargent LL, King TJ (1991) The conservation of dinucleotide microsatellites among mammalian genomes allows the use of heterologous PCR primer pairs in closely related species. Genomics, 10,654-660. |
| [18] | Morgan A, Carthew SM, Sedgley M (2002) Breeding system, reproductive efficiency and weed potential of Acacia baileyana. Australian Journal of Botany, 50,357-364. |
| [19] | Nei M (1987) Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York. |
| [20] | Ng CH, Koh SC, Lee SL, Ng KKS, Mark A, Norwati M, Wickneswari R (2005) Isolation of 15 polymorphic microsatellite loci in Acacia hybris (Acacia mangium×Acacia auriculiformis) . Molecular Ecology Notes, 5,572-575. |
| [21] | Oballa PO (1993) Genetic Variation Within Acacia karroo Hayne. PhD thesis. 224pp. Oxford Forestry Institute (OFI), Oxford, UK. |
| [22] | Otero-Arnaiz A, Schnabel A, Glenn TC, Schable NA, Hagen C, Ndong L (2005) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers in the East African tree, Acacia brevispica (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) . Molecular Ecology Notes, 5,366-368. |
| [23] | Pan Q (潘奇) (2004) Artificial cultivation of Acacia pennata. Yunnan Agriculture (云南农业), 11,7. (in Chinese) |
| [24] | Peakall R, Smouse PE (2001) GenAlEx 5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research. Australian National University, Canberna, Australia. |
| [25] | Ross JH (1979) A conspectus of the African Acacia species . Memoirs of Botanical Survey of South Africa, 44,155. |
| [26] | Rossetto M (2001) Sourcing of SSR markers from related plant species. In:Plant Genotyping: The DNA Fingerprinting of Plants(ed. Henry RJ), pp.211-224. |
| [27] | Thelma B, Clarisse PS, Gecele MP, Fernanda B, Michael FF, Christian L (2007) Cross-species transfer of nuclear microsatellite markers: potential and limitations. Molecular Ecology, 16,3759-3767. |
| [28] | Wang L (王丽), Zhao GF (赵桂仿) (2005) Microsatellite primers shared by different plant species and genera. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica (西北植物学报), 25,1540-1546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Wang JR (王洁如), Long CL (龙春林) (1995) Enthnobotany study of traditional edible plants of Jinuo nationality. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 17,161-168.. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Wardill TJ, Scott KD, Graham GC, Zalucki MP (2004) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci from Acacia nilotica ssp . indica (Mimosaceae ). Molecular Ecology Notes, 4,361-363. |
| [31] | Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution, 38,1358-1370. |
| [32] | Wright S (1951) The genetical structure of populations. Annals of Eugenics, 15,323-354. |
| [33] | Xu YK (许又凯), Liu HM (刘宏茂), Dao XS (刀祥生), Xu ZY (许自艳) (2004) The study on the nutritional contents of Acacia pennata and its evaluation as a wild vegetable . Guihaia (广西植物), 24,12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Xu XL (徐小林), Xu LA (徐立安), Huang MR (黄敏仁), Wang ZR (王章荣) (2004) Genetic diversity of microsatellite (SSR) of natural populations of Quercus variabilis. Hereditas (Beijing) (遗传), 26,683-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Yang QW (杨庆文), Yu LQ (余丽琴), Zhang WX (张万霞), Chen DZ (陈大洲), Shi JX (时津霞), Ren JF (任军方), Miao H (苗晗) (2005) Comparative studies on genetic diversities between in-situ and ex-situ conserved germplasm of Oryza rufipogon. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 38,1073-1079. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Zhang FM (张富民), Ge S (葛颂) (2002) Data analysis in population genetics.Ⅰ. Analysis of RAPD data with AMOVA. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 10,438-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Zhang JR (张金然), Shang J (尚洁), Wang QY (王秋玉) (2006) Genetic diversity among the clones of aspen hybrid detected by simple sequence repeat DNA marker. Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 26,447-451, 460. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Zhao HK (赵洪锟), Wang YM (王玉民), Li QY (李启云), Zhang M (张明), Zhuang BC (庄炳昌) (2001) SSR analysis of wild soybean and cultivated soybean from different latitude in China. Soybean Science (大豆科学), 20,172-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Zeng J, Zou YP, Bai JY, Zheng HS (2002) Preparation of total DNA from ‘recalcitrant plant taxa’. Acta Botanica Sinica (植物学报), 44,694-697. |
| [1] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [4] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [5] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [6] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [7] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [8] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [9] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [10] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [11] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [12] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [13] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [14] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| [15] | 苏金源, 燕语, 李冲, 李丹, 杜芳. 通过遗传多样性探讨极小种群野生植物的致濒机理及保护策略: 以裸子植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 376-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
